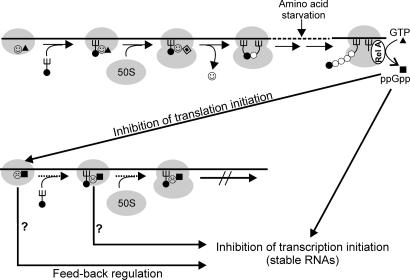
Fig. 6.
Schematic representation of the postulated regulatory circuits involving IF2 and ppGpp. (Upper) The essential steps of translation initiation: formation of 30SIC in the presence of IF2-GTP (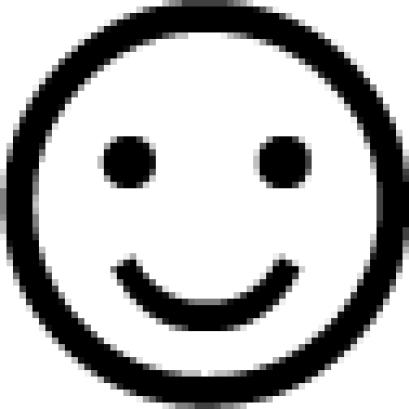 ▴), association of 50S subunit and formation of 70SIC, GTP (▴) hydrolysis to GDP (
▴), association of 50S subunit and formation of 70SIC, GTP (▴) hydrolysis to GDP ( ), IF2 dissociation (
), IF2 dissociation ( ), and initiation dipeptide formation. Amino acid starvation during elongation triggers RelA-dependent synthesis of ppGpp (■), which inhibits stable RNA transcription (Lower) and, as shown in this study, the initiation functions of IF2 (30SIC formation and initiation dipeptide formation). A possible function of translation initiation intermediates containing IF2-ppGpp (
), and initiation dipeptide formation. Amino acid starvation during elongation triggers RelA-dependent synthesis of ppGpp (■), which inhibits stable RNA transcription (Lower) and, as shown in this study, the initiation functions of IF2 (30SIC formation and initiation dipeptide formation). A possible function of translation initiation intermediates containing IF2-ppGpp ( ) in feedback inhibition of stable RNA transcription is suggested by earlier reports that components of the translation initiation apparatus play an active part in this regulation. In particular, IF2, fMet-tRNA, and ppGpp were found to interact with the RNA polymerase and influence its activity at stable RNA promoters (38, 39), whereas IF2 (40), IF3 (41), and initiation-competent 30S subunits (42) were shown to be required for feedback repression of stable RNA transcription.
) in feedback inhibition of stable RNA transcription is suggested by earlier reports that components of the translation initiation apparatus play an active part in this regulation. In particular, IF2, fMet-tRNA, and ppGpp were found to interact with the RNA polymerase and influence its activity at stable RNA promoters (38, 39), whereas IF2 (40), IF3 (41), and initiation-competent 30S subunits (42) were shown to be required for feedback repression of stable RNA transcription.