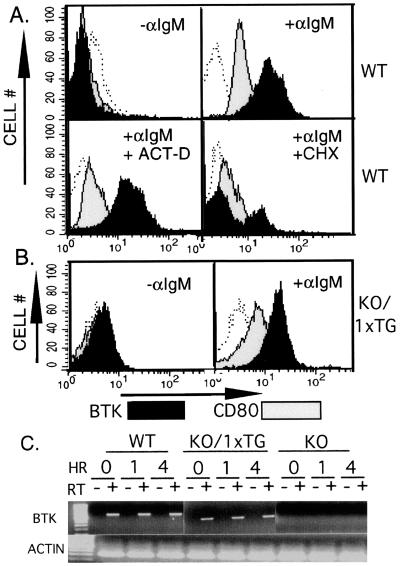
Figure 5.
(A) Up-regulation of Btk by a posttranscriptional mechanism. Wild-type splenic B lymphocytes were stimulated by cross-linking BCR with anti-IgM (20 μg/ml) for 4 hours in the presence of cycloheximide (100 μM), actinomycin D (100 μM), or carrier (DMSO 1%) alone as indicated. Cells were fixed and immunostained with a nonspecific antibody (open histograms), anti-Btk (filled histograms), or anti-CD80 (gray histograms) followed by the appropriate fluorescent-tagged secondary antibody. (B) Up-regulation of transgenic Btk protein after BCR crosslinking. Splenic B lymphocytes expressing a single copy of the Btk transgene (KO/1 × TG) were stimulated by cross-linking BCR with anti-IgM (20 μg/ml) for 4 hours as indicated. Cells were fixed and immunostained with a nonspecific antibody (open histograms), anti-Btk (filled histograms), or anti-CD80 (gray histogram) followed by the appropriate fluorescent-tagged secondary antibody. (C) Semiquantitative assay of Btk mRNA. Splenic B lymphocytes expressing endogenous Btk (WT), a single copy of the Btk transgene (KO/1 × TG), or no detectable Btk protein (KO) were stimulated by cross-linking BCR with anti-IgM (20 μg/ml) for 0, 1, or 4 hours as indicated. Total RNA was purified from the cells and was tested (0.8–3.2 μg/sample) for Btk mRNA expression before (−) and after (+) reverse transcription (RT) of the RNA sample. RT was performed by using oligo(dT) primer. PCR was then performed for 35 cycles using Btk-specific sense (bp 781–799, gctgaaaaaggtcgtggc) and antisense (bp 1,517–1,500, cttcgaccacgtcaacat) primers. The results shown were obtained by using 3.2 μg of total RNA per sample. Actin RNA transcripts were amplified (+ RT condition only) to demonstrate the integrity of the RNA samples (Lower).