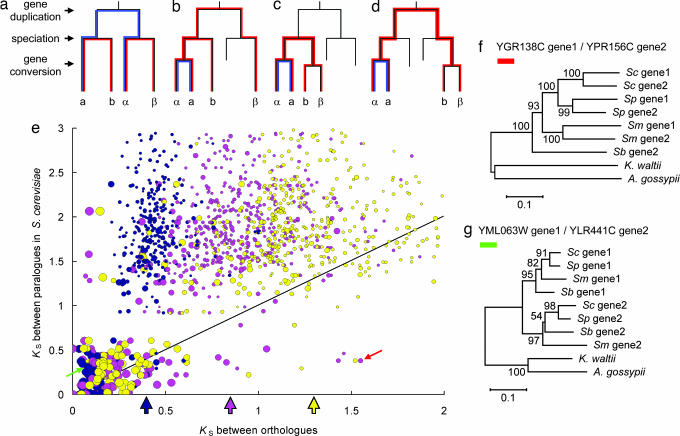
Fig. 1.
Effects of gene conversion on tree topology and observed patterns of synonymous distances between orthologous or between paralogous genes. (a) Genes a and α (b and β) are paralogues derived from a gene duplication, and a and b (α and β) are orthologues derived from a speciation event. Blue and red lines indicate the distances between paralogues (a and α) and orthologues, respectively. (b) α was converted by a. (c) α was converted by a, and β was converted by b. (d) α was converted by a, and b was converted by β. Note that gene conversion can reduce the distance between paralogues but tends to increase the distance between syntenic orthologues. (e) KS between paralogues in S. cerevisiae (distance between a and α) vs. KS between orthologues (distances between a and b or α and β). Dark blue, S. cerevisiae vs. S. paradoxus; pink, S. cerevisiae vs. S. mikatae; yellow, S. cerevisiae vs. S. bayanus; open arrows indicate the average distances for these species pairs under weak codon-usage bias (KS = 0.4, 0.8, and 1.3). Circle sizes indicate the CAI values of the genes in S. cerevisiae. The slope line indicates that the distance between paralogues is equal to that between orthologues. The red and green solid arrows indicate gene pairs YGR138C/YPR156C between S. cerevisiae and S. mikatae and YML063W/YLR441C between S. cerevisiae and S. paradoxus, respectively. Genes with incomplete sequences, paralogous pairs with KS > 3, and orthologous pairs with KS > 2 are not included in this figure. (f) Neighbor-joining tree (KS distances) of the WGD gene pair YGR138C/YPR156C in S. cerevisiae (Sc), their orthologues in S. paradoxus (Sp), S. mikatae (Sm), and S. bayanus (Sb), and the outgroups in K. waltii (3) and A. gossypii (11) (the red arrow in 1e, CAI = 0.310/0.261). The orthologue of YGR138C in S. bayanus was not completely sequenced and not included in this figure. (g) YML063W/YLR441C (the green arrow, CAI = 0.769/0.696). The numbers at branch nodes are bootstrap values.