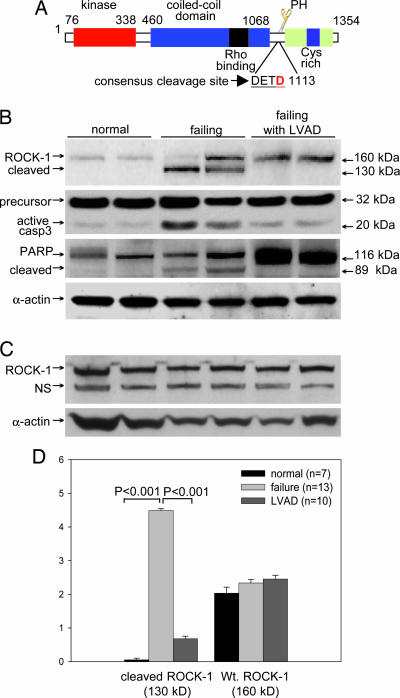
Fig. 1.
ROCK-1 cleaved in human failing hearts. (A) A schematic diagram of ROCK-1 structural domains. The caspase-3 consensus cleavage sequence (DETD, amino acids 1110–1113) is conserved among ROCK-1 genes in mammals. Cleavage of ROCK-1 removes the inhibitory C terminus, generating a 130-kDa fragment with constitutive kinase activity. (B) Representative Western blots of human myocardial samples. ROCK-1 protein levels were assessed from myocardial samples taken from patients with end-stage heart failure with and/or without LVAD treatment and from normal hearts. An increase in caspase-3 activity was observed in human failing hearts, which returned to control levels after LVAD treatment. Cleavage of PARP, a known caspase-3 substrate during apoptosis, is also shown as an internal control. Even protein loading for PAGE was shown by a blot probed with a specific antibody against α-actin. (C) A specific antibody directed against the C-terminal end of ROCK-1 detected only full-length ROCK-1 in all patient groups. NS, nonspecific. (D) Densitometric analysis of cleaved ROCK-1 and full-length ROCK-1 levels were taken from two to three replicates that covered 13 heart failure patients, 10 LVAD patients, and 10 noncardiac disease control patients. The statistical analysis showed a significant difference (P < 0.001) in comparison between failing myocardium samples and normal myocardium samples in the cleaved ROCK-1 subspecies (130 kDa).