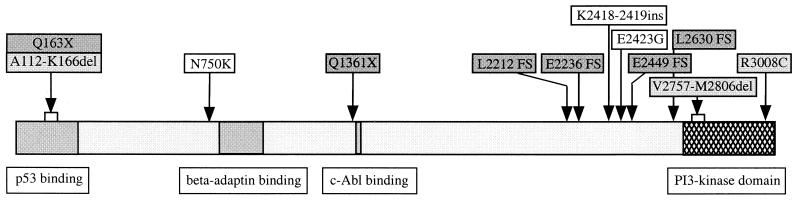
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the ATM protein including the location of mutations detected in different MCLs with respect to the domains that are responsible for the kinase function (21, 44) and the binding of p53 (46), β-adaptin (47), and c-Abl (28, 29). The positions of the mutations are indicated by arrows. Dark-gray boxes represent truncating mutations (X, new stop codon; FS, frameshift leading to truncation). Mutations that correspond to A-T alleles and/or mutations associated with T-PLL are displayed in light gray: R3008C has been described as an A-T allele (48) and as a mutation in two T-PLL cases (34, 37); the splice-site mutations in MCL-J and MCL-A both resemble A-T mutations, which cause skipping of exons 7 and 59 from the transcript, respectively (42, 49–51). Note that the nucleotide change causative for exon 7 skipping and the deletion of 55 aa (A112-L166del) created a new stop codon (Q163X) in the low level of correctly spliced transcripts produced from this allele. Mutations in unshaded boxes are amino acid changes, the functional consequences of which are not yet known.