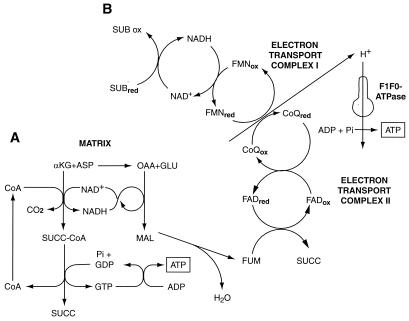
Figure 2.
Metabolic pathways for anaerobic generation of ATP promoted by αKG/ASP. (A) During hypoxia, αKG is metabolized to succinate (SUCC), forming GTP by substrate-level phosphorylation. GTP is transphosphorylated to ATP. Transamination of αKG to glutamate by aspartate provides oxalacetate (OAA). Conversion of OAA to malate (MAL) and fumarate (FUM) is linked to decarboxylation of αKG by the NAD-NADH redox couple (22). (B) Reduction of fumarate to succinate is coupled to oxidation of reduced ubiquinone (CoQred) generated via NADH by reducing equivalents from substrate (SUB) oxidation in the citric acid cycle (e.g., A) (21). This process anaerobically maintains electron flux and proton extrusion in complex I with ATP production by the mitochondrial inner membrane F1F0-ATPase. (Figure modified from ref. 25 with permission.)