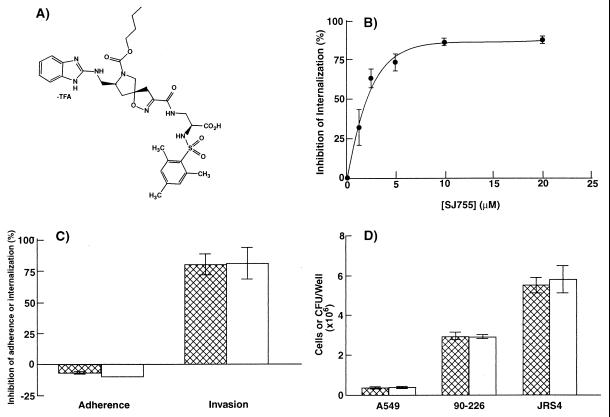
Figure 1.
Inhibition of streptococcal invasion by the integrin α5β1 antagonist, SJ755. (A) Chemical structure of SJ755 ((S,S,S,)-2-[(2, 4, 6-trimethylphenyl) sulfonylamino-3-[[7-n-butoxycarbonyl-8- [(benzimidazol-2-ylamino)methyl]-1-oxa-2,7-diazaspiro- [4,4]-non-2-en-3-yl]carbonylamino] propionic acid, trifluoroacetate). (B) Internalization of S. pyogenes 90-226 by A549 cells vs. SJ755 concentration. (C) Effects of 10 μM SJ755 on bacterial adherence to and internalization by A549 human lung epithelial cells. Hatched bars, strain 90-226 (M1+, PrtF1−); open bars, JRS4 (M6+, PrtF1+). (D) Effect of SJ755 on bacterial viability and adherence of A549 cells to the substratum. Hatched bars, medium contained 0.5% DMSO; open bars, medium contained 10 μm SJ755, 0.5% DMSO. All data are the means ± SEM of three independent experiments, in which each assay was performed in triplicate (i.e., n = 9). In the absence of SJ755, percent internalization was 33.1 ± 5.4 for strain 90-226 and 11.5 ± 1.0 for strain JRS4.