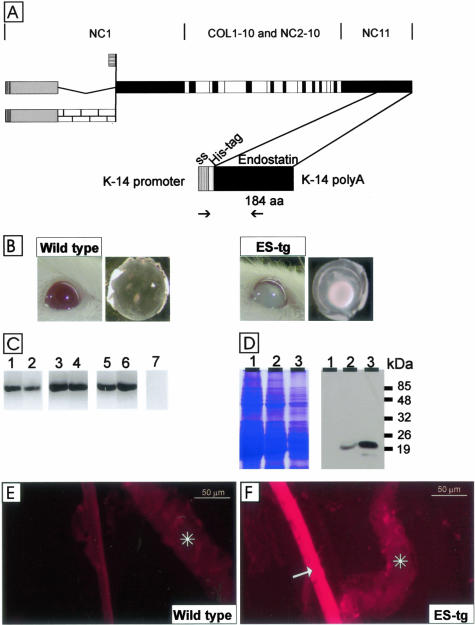
Figure 1.
A: Polypeptide structures of type XVIII collagen and the transgenic endostatin construct. The top part shows the schematic structure of the full-length variants of the mouse α1(XVIII) chain. Collagenous sequences are shown in white, noncollagenous domains common to all variants are shown in black, noncollagenous sequences common to both long variants are shown in gray, and a noncollagenous sequence specific to the longest variant is shown with a brick pattern. The bottom part shows the schematic structure of the transgene product. The cDNA encoding a 184-residue endostatin sequence (aa) starting with residues HTH and preceded by a tag of six His-residues and a signal sequence (ss) was inserted between the K14 promoter and a polyA tail. The locations of the primers used for RT-PCR are indicated by arrows. B: Opacity of the lens in a 12-month-old J4 transgenic mouse (ES-tg) and a nuclear cataract in a lens dissected from a 5-month-old J4 mouse. Age-matched controls are also show. C: RT-PCR analysis of transgene-derived endostatin expression in whole eyes of mice of lines K18 (lanes 1 and 2), G20 (lanes 3 and 4), and J4 (lanes 5 and 6) at ages of 3 months (lanes 1, 3, and 5) and 8 months (lanes 2, 4, and 6) with primers specific for the transgene product. A control reaction (lane 7) with wild-type RNA was negative. D: Transgene expression in the eyes of mouse lines K18 (lane 1), G20 (lane 2), and J4 (lane 3) was analyzed by Western blotting (right). Equal loading of protein samples was verified by Coomassie staining (left). The anti-endostatin antibody recognized a major 20-kd fragment in 3-month-old transgenic mouse lines G20 and J4. E and F: Localization of transgenic endostatin in the lens capsule. Immunofluorescence stainings of samples from wild-type mice (E) and J4 mice (F) with the His-tag antibody. The His-tag antibody stained the whole lens capsule in the transgenic mouse, but no staining was detected in the wild-type mouse. Scale bars, 50 μm. Asterisks, iris.