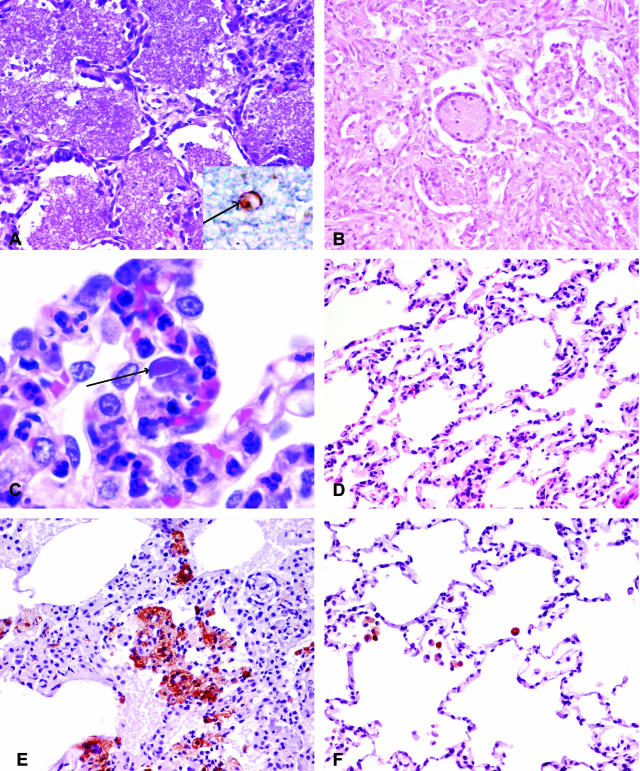
Figure 1.
A-D: Pathological changes in the lungs of SHIV-infected macaques stained with H&E. A: Lung section from SHIV-infected macaque with pneumonia (macaque RHU5) showing diffuse alveolar accumulations of pink flocculent material typical of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (×20). The inset shows the immunohistochemical staining of Pneumocystis carinii (arrow). B: Lung section from SHIV-infected macaque with pneumonia (macaque PJX) showing diffuse interstitial and alveolar pneumonia. Both the interstitium and alveoli are infiltrated with inflammatory macrophages and syncytial cells (×20). C: Higher power of the lung section from SHIV-infected macaque with pneumonia (macaque PWJ) showing inflammation with foamy macrophages and cells containing intranuclear inclusion bodies (arrow) (×100). D: Section of SHIV-infected, uninflamed lung (macaque RHT5) showing no expansion of alveolar septa and no alveolar infiltrates (×20). E: Lung section from SHIV-infected macaque with pneumonia (macaque PJX) stained with macrophage-specific antibody, Ham56, demonstrating massive influx of macrophages compared to (F) lung section of SHIV-infected macaques without pneumonia (macaque PHP) (×20).