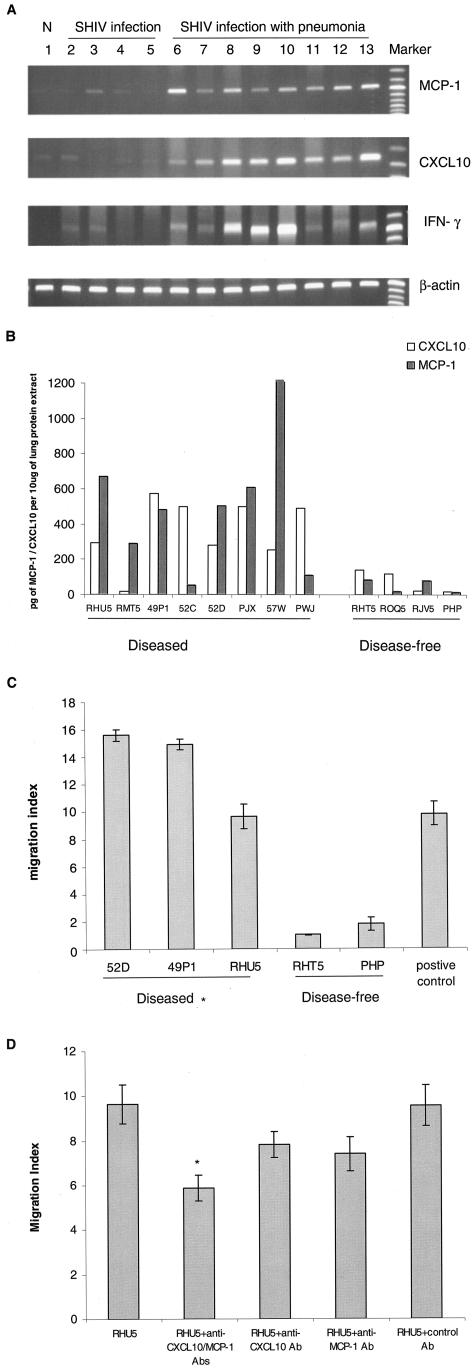
Figure 3.
A: RT-PCR analysis of MCP-1, CXCL10, and IFN-γ in the lungs of SHIV-infected macaques. Sample of lung RNA from a representative normal, uninfected macaque (lane 1), from four SHIV-infected macaques without pneumonia (lanes 2 to 5, macaques RHT5, RJV5, ROQ5, PHP, respectively); and from eight SHIV-infected macaques with pneumonia (lanes 6 to 13, macaques 57W, RMT5, PWJ, 52C, 52D, RHU5, 49P1, and PJX, respectively) were subjected to RT-PCR analysis using primers specific for macaque MCP-1, CXCL10, IFN-γ, and β-actin. B: MCP-1 and CXCL10 protein analysis in the lungs of SHIV-infected macaques. Equal amounts of proteins extracted from lung tissues were used to determine the MCP-1 and CXCL10 protein levels by ELISA kit. C: Chemotactic analysis of lung protein extract from SHIV-infected macaques. Thirty μl of lung protein extract from macaques 52D, 49P1, and RHU5 (SHIV-pneumonia group) and macaques RHT5 and PHP (SHIV-non-pneumonia group) were used for the chemotactic assay. Macaque PBMCs migrating toward the lung proteins were counted by using Cell Titer 96 Aqueous One Solution Assay. Migration index was calculated as the number of cells migrating toward the protein extract from the diseased or control macaque lungs divided by the number of cells migrating toward PBS only. 10 ng/ml of MCP-1 was used as positive control. *, SHIV-pneumonia group (52D, 49P1, or RHU5) is statistically significant compared to SHIV-non-pneumonia group (RHT5, PHP), P < 0.001. D: For blocking experiments, lung homogenate from a representative macaque with SHIV-pneumonia (RHU5, similar result was also obtained from macaque 52D) was either untreated or preincubated for 1 hour with MCP-1 and/or CXCL10 neutralizing antibodies followed by chemotactic assay. Control antibody included mouse isotype IgG. *, statistical significance of migration index of antibody-treated homogenates compared to that of the untreated homogenate.