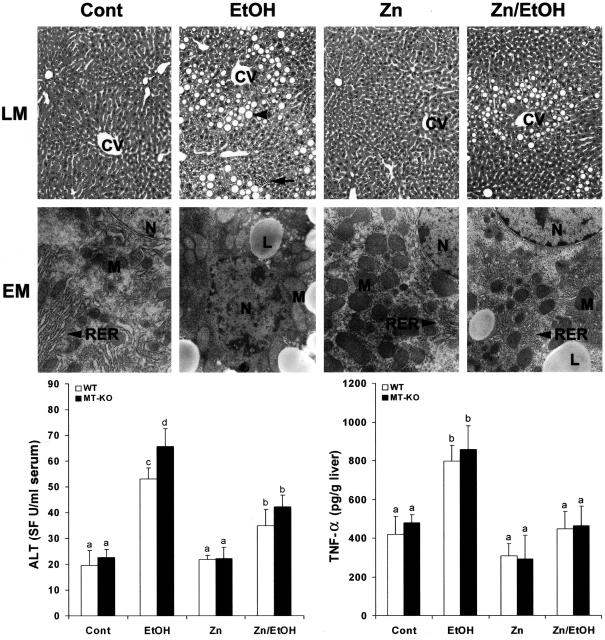
Figure 3.
Effects of zinc supplementation on liver injury in MT-KO and WT 129/Sv mice chronically fed ethanol for 12 weeks. Light microscopy (LM) shows prominent steatosis (arrowhead) and inflammation (arrow) in the liver of ethanol-fed mice, but these histopathological changes were primarily inhibited by zinc. H&E stain. Electron microscopy (EM) reveals ultrastructural alterations in the hepatocytes, including accumulation of lipid droplets (LD), enlargement and degeneration of mitochondria (M), disorganization of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and condensation of chromatin in the nucleus (N). All these ultrastructural changes were suppressed by zinc. Serum ALT activities were measured using a Sigma Diagnostics kit. Hepatic TNF-α levels were measured using an ELISA kit. Results in serum ALT and hepatic TNF-α levels are means ± SD (n = 4 to 6). Significant difference (P < 0.05) is identified by different letters. CV, Central vein; Cont, control; EtOH, ethanol. Original magnifications: [times130 (LM row); ×9800 (EM row).