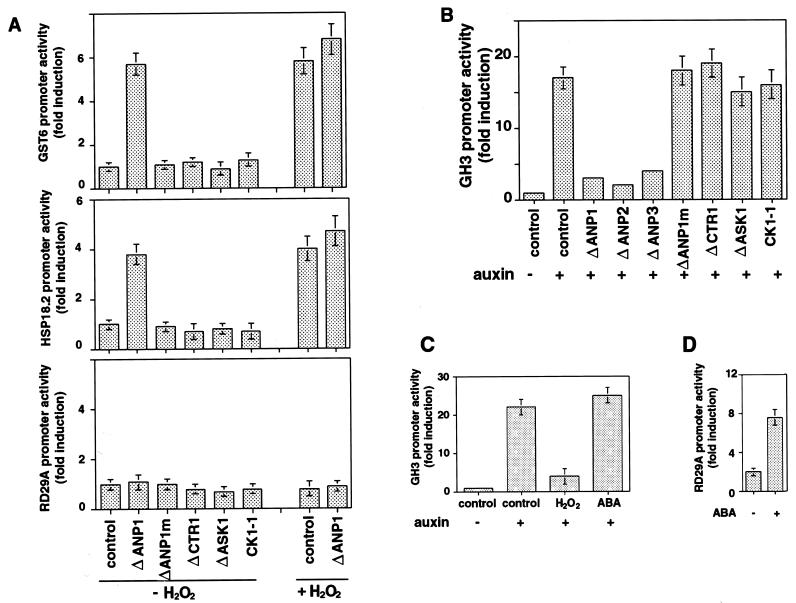
Figure 3.
The ANP pathway represents a molecular link between stress and auxin signaling. (A) ANP1 activates oxidative stress-inducible gene expression. Arabidopsis protoplasts were cotransfected with one of the reporter constructs: GST6-LUC (GST6), HSP18.2-LUC (HSP18.2), or RD29A-LUC (RD29A) and one of the ANP constructs as described in the legend of Fig. 2A. Other control kinase constructs were the catalytic domains of CTR1 (ΔCTR1), ASK1 (ΔASK1), and CK1-1 (CK1-1). Vector DNA was used as a control (control). The transfected protoplasts were incubated for 3 h to allow kinase expression before 200 μM H2O2 was added to induce the GST6 and HSP18.2 promoters. The cells were incubated for another 3 h before the promoter activities were measured. (B) ANPs repress the auxin response. Arabidopsis protoplasts were cotransfected with the GH3-LUC reporter construct and one of the kinase constructs as described in the legends of Figs. 2A and 3A. The transfected protoplasts were incubated for 3 h to allow kinase expression before 1 μM 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (auxin) was added to induce the GH3 promoter. The cells were incubated for another 3 h before the GH3 promoter activity was measured. (C) H2O2 suppresses the auxin-responsive GH3 promoter. Arabidopsis protoplasts were transfected with the GH3-LUC reporter construct and incubated in the absence (− auxin) or presence of 1 μM 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (+ auxin) and 200 μM H2O2, or 100 μM ABA for 3 h before activity of the GH3 promoter was measured. (D) ABA induces the RD29A promoter. Arabidopsis protoplasts were transfected with the RD29A-LUC reporter construct and incubated in the absence or presence of 100 μM ABA for 3 h before activity of the RD29A promoter was measured. All data presented on the figure are the results of triplicate samples and three independent experiments.