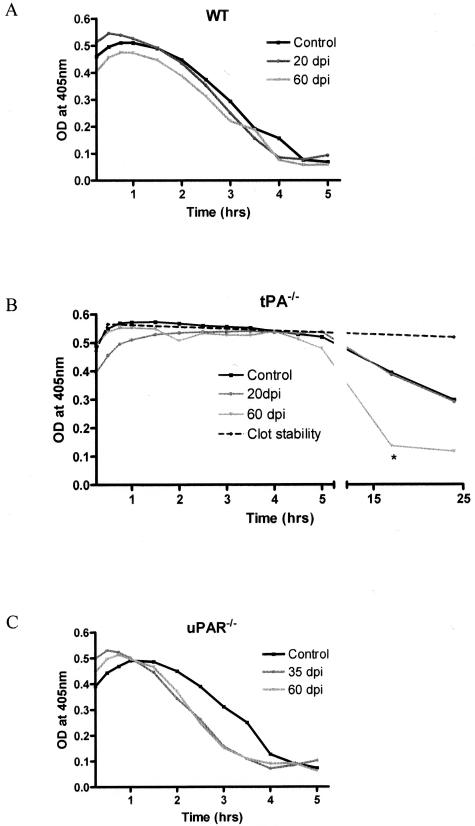
Figure 7.
Fibrinolysis in the mouse CNS. Spinal cords from control and EAE mice at specific time points were homogenized for protein extraction. The fibrinolytic capacity was investigated using a clot lysis assay that measures the degradation of an in vitro-formed clot using spectrophotometry. Results are presented as the mean clot degradation over time for WT (A), tPA−/− (B), and uPAR−/− (C) mice. Samples from tPA−/− mice were incubated for a further 20 hours to detect fibrinolysis initiated by uPA. tPA−/− mice at 60 dpi had a significantly faster clot degradation than either control or 20 dpi mice. *P < 0.05.