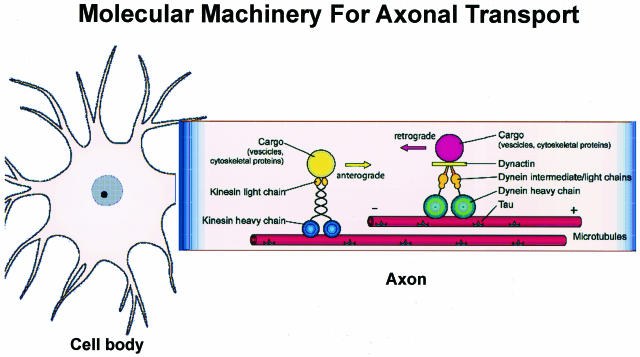
Figure 2.
The molecular machinery underlying mechanisms of anterograde (directed toward the + end of MTs) and retrograde (directed toward the − end of MTs) axonal transport in neurons by kinesin and dynein motor proteins, respectively, is schematically illustrated. Kinesins and dyneins and other motor-associated proteins move on MTs to transport Golgi-derived vesicles, cytosolic protein complexes, cytoskeletal polymers, and so forth (for further details and additional citations, see Roy et al15).