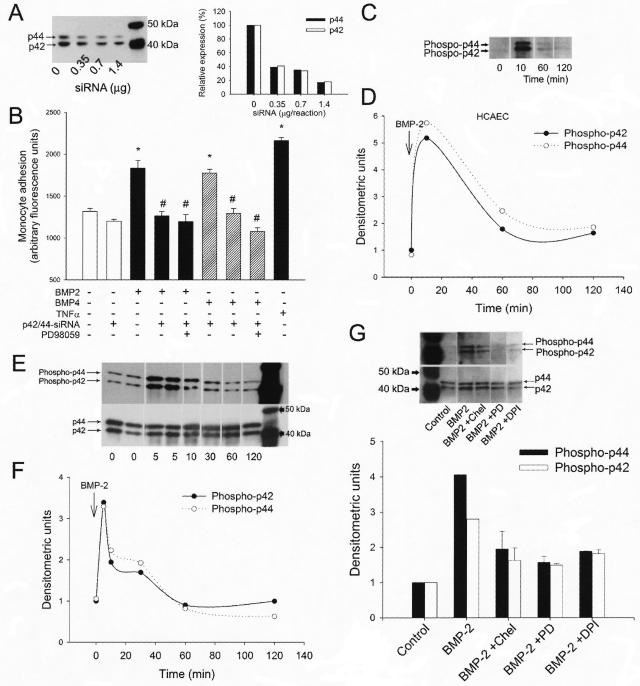
Figure 7.
A: Representative Western blot (left) and densitometric data (right) showing the effect of increasing concentrations of anti-p42/p44 siRNAs on the expression of p42/44 MAP kinase in primary human coronary arterial endothelial cells (HCAECs). B: Effect of pretreatment with anti-p42/p44 siRNAs on BMP-2- and BMP-4- (10 ng/ml, for 2 hours) induced adhesion of fluorescently labeled PMA-stimulated monocytes to HCAECs. PD98059 (30 minutes, 10 μmol/L) was used to pharmacologically inhibit MAP kinase activity. TNF-α (10 ng/ml) was used as positive control. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus control, #P < 0.05 versus BMP-2/4 treatment. C–F: Representative Western blots (C, E) and densitometric data (D, F) showing the time course of p42/44 MAP kinase phosphorylation in BMP-2 (10 ng/ml)-treated HCAECs (C, D) and rat carotid arterial segments (E, F). G: Representative Western blot (top) and densitometric data (bottom) showing BMP-2 (10 ng/ml, 10 minutes)-induced phosphorylation of p42/44 MAP kinase in HCAECs pretreated with DPI, chelerythrine, and PD98059.