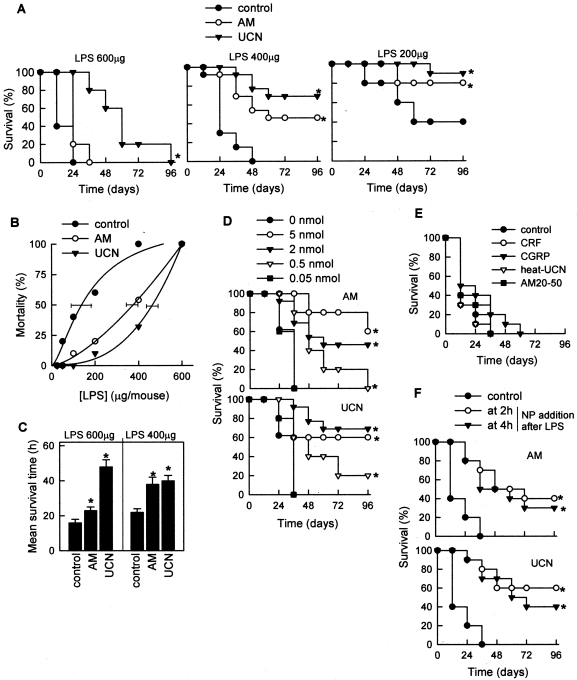
Figure 2.
Treatment with UCN or AM protects against lethal endotoxemia. A–C: BALB/c mice were injected i.p. with different doses of LPS (control). AM or UCN (2 nmol/mouse) was injected i.p. 30 minutes after LPS administration. Survival was monitored over the next 96 hours. Similar results were obtained in three identical independent experiments or when C57BL/6 mice were used. Mortality curves in B were used to calculate LD50, and horizontal bars indicate the 95% confidence limits of LD50 determinations. In C, the average survival time was calculated for nonsurvivors in both the untreated and UCN/AM-treated groups. D: Mice were injected i.p. with 400 μg of LPS and different doses of UCN or AM (from 0 to 5 nmol/animal). E: Mice were injected i.p. with 400 μg of LPS and 30 minutes later, treated with medium (control), CRF, CGRP, or heat-inactivated UCN or the AM-fragment AM20–50 (2 nmol/mouse). Survival was monitored over the next 96 hours. F: UCN or AM (2 nmol/mouse) was injected i.p. 2 or 4 hours after LPS challenge. n = 12–20 mice/group. *P < 0.001 versus untreated control mice.