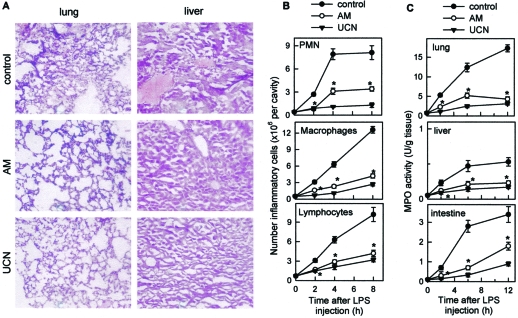
Figure 3.
AM and UCN reduce endotoxemia-associated histopathology. Mice were injected i.p. with LPS (control). UCN or AM (2 nmol/mouse) was administered i.p. 30 minutes after LPS administration. A: UCN and AM reduced inflammatory infiltration and disseminated coagulation in target organs. Histopathology analysis was determined in hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of lung and liver obtained at 24 hours of disease (×150). B: UCN and AM reduce leukocyte recruitment in the peritoneal cavity. Peritoneal cell suspensions were obtained at different times after LPS injection, and numbers of macrophages, lymphocytes, and PMNs were determined by flow cytometry. C: UCN and AM decrease MPO activity in lungs, liver, and intestine. MPO content was determined at different times after LPS infusion. n = 8–12 mice/group. *P < 0.001 versus untreated control mice.