Fig. 2.
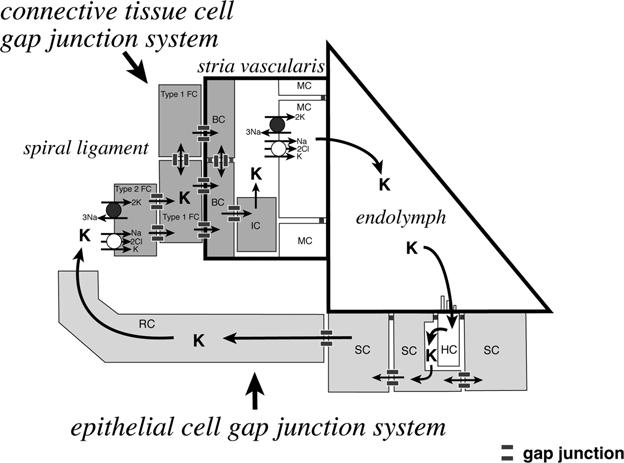
Schematic illustration of a potassium ion recycling mechanism in the mammalian cochlea. There are two independent gap junction systems, the epithelial cell gap junction system and the connective tissue cell gap junction system in the cochlea. Potassium ions, which play a pivotal role in the mechanoelectrical sound transduction process in the cochlea, are recycled via these two gap junction systems. BC, basal cells; HC, hair cells; IC, intermediate cells, MC, marginal cells; RC, root cells; SC, supporting cells; Type 1 FC, type I fibrocytes; Type II FC, type II fibrocytes. This illustration is modified with permission from Kikuchi et al. (2000a).
