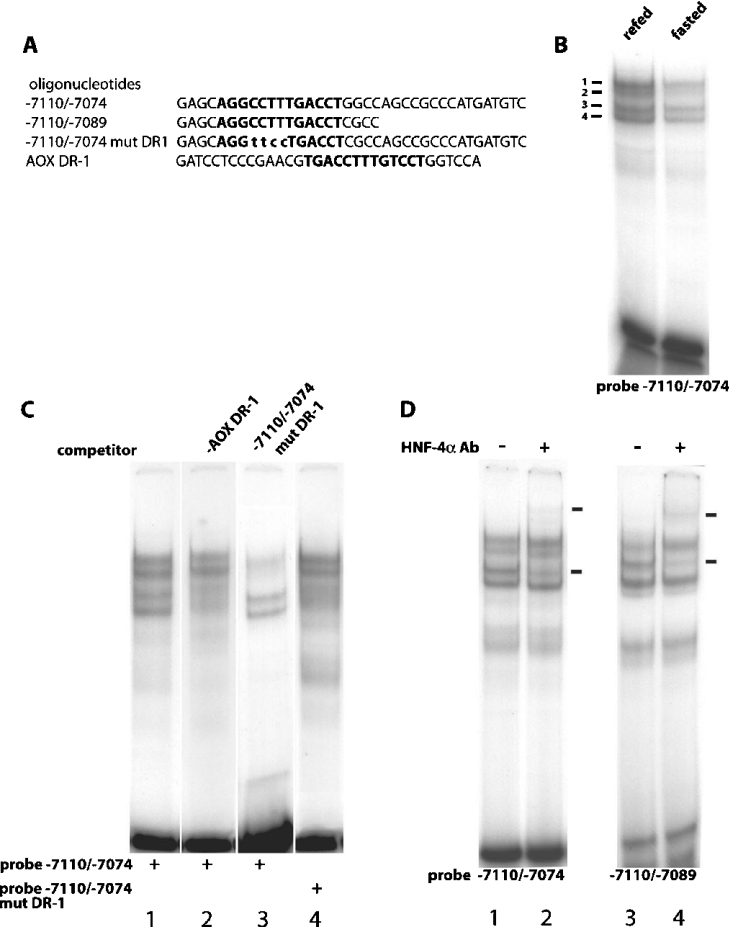
Figure 2. HNF-4α binds the FAS DR-1 element.
(A) Sequences of the oligonucleotides used as probes and competitors in the gel-shift reactions. The sequence of the DR-1 elements are highlighted in boldface and the mutated bases in the −7110/−7074 mut DR-1 are displayed in lower-case. (B) 1.0 ng of −7110/−7074 radiolabelled oligonucleotide was incubated with either 5 μg of fasted or refed liver nuclear extract and subjected to electrophoresis on a 5% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel. (C) All gel-shift reactions were incubated with 5 μg of refed liver nuclear extract and employed the following radiolabelled oligonucleotides: −7110/−7074 (lanes 1, 2 and 3) and −7110/−7074 mut DR1 (lane 4). The competing oligonucleotides AOX DR-1 (lane 2) and −7110/−7074 mut DR1 (lane 3) were added at 100× molar excess to the binding reaction. (D) Immunological characterization of HNF-4α binding to the DR-1 element. Gel-shift reactions included 5 μg of refed liver nuclear extract and employed the following radiolabelled oligonucleotides: −7110/−7074 (lanes 1 and 2) and −7110/−7089 (lanes 3 and 4). Antibody (Ab) directed against HNF-4α was added and arrows indicate positions of specific complexes.