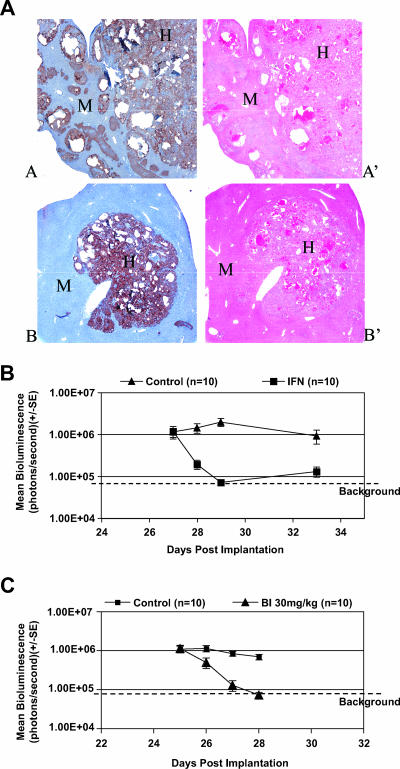
FIG. 4.
Anti-HCV activity of IFN-α 2b and BILN 2061 in the intrahepatic mouse efficacy model. (A) Histology of a chimeric liver. Hematoxylin and eosin staining (A′ and B′) allows identification of the human hepatoma T7-11 cells (H) within mouse (M) parenchyma. Clusters of human T7-11 cells can also be visualized with antibody specific for human mitochondria (A and B) shown in brown. (B) Antiviral effect of IFN-α 2b (IFN). T7-11 cells were implanted directly into the parenchyma of liver in γ-irradiated SCID mice. IFN treatment was given SC once daily for 2 days starting on day 27 postimplantation. A dose of 15,000 IU/mouse/day of IFN was given to the treated group, and 10 μg/mouse/day of human albumin was given to the control group. (C) Antiviral effect of BILN 2061 (BI). A treatment of 30 mg/kg of BILN 2061 was initiated once daily subcutaneously for 3 days starting on day 25 postintrahepatic implantation. Individual mice were imaged daily prior to each day's treatment on days 25 through 28. Error bars indicate standard error (SE).