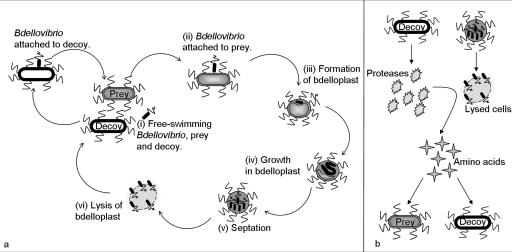
FIG. 1.
Bdellovibrio life cycle and interactions occurring during the predation experiments. (a) Biphasic life cycle of B. bacteriovorus, showing the direct effect on predation caused by the Bacillus decoy occupying B. bacteriovorus in nonproductive attachments which reduce the availability of attack-phase predator cells to attach productively to prey cells. (b) Interactions between the B. subtilis decoy and the E. coli prey, including production of proteases, which degrade lysed bdelloplasts into their constituent amino acids, generating nutrients for both prey and decoy.