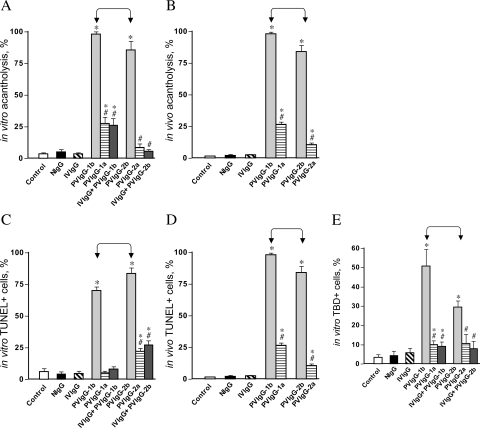
Figure 2.
Effects of PVIgG and normal IgGs on keratinocyte acantholysis and cell death. Keratinocyte monolayers were treated with test IgGs as described in the legend to Figure 1, except that two IVIgG samples were combined. The same IgG samples were injected intraperitoneally to 1-day-old BALB/c mice at the total dose of 0.1 mg/g body weight. Control monolayers and mice were left intact (C). The extent of acantholysis and the occurrence of cell death markers were examined in keratinocyte monolayers 48 hours after exposure and in specimens of mouse skin 24 hours after passive IgG transfer, as described in Materials and Methods. *, significant (P < 0.05) differences from control. #, statistical significance (P < 0.05) compared with the results obtained with PVIgG alone. Significant differences between specific experimental conditions are indicated in the graph with pointed square brackets. A: Extent of acantholysis in keratinocyte monolayers. B: Extent of acantholysis in mouse epidermis. C: Relative number of TUNEL+ keratinocytes in the monolayers. D: Relative number of TUNEL+ keratinocytes in mouse epidermis. E: Relative number of TBD+ keratinocytes in the monolayers.