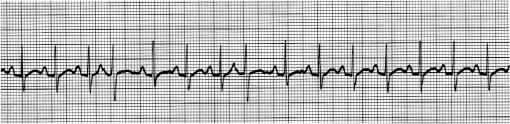
Figure 12.
Premature atrial and junctional complexes. Most cycles commence with a P wave, and most PR intervals are normal. Therefore, the rhythm is sinus-paced, but occasionally an extra impulse is fired from an ectopic pacemaker that travels down into the ventricle and creates an extra QRS complex. Notice that normally there is a pause, or a period of time following a T wave until the next P wave commences. In the case of premature complexes, this pause is interrupted. At this point in your training, it is not important to interpret the source of this premature complex; is it atrial or junctional? We know it is coming from above the ventricle, and it is always acceptable to call it a premature atrial complex. The difference between the two has little clinical relevance.