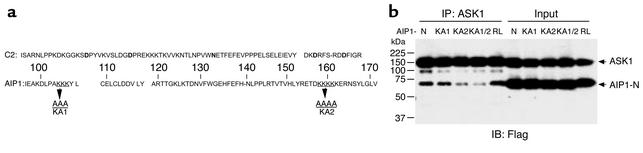
Figure 2.
A lysine-rich cluster within the C2 domain of AIP1 is critical for ASK1 binding. (a) Sequence alignment of C2 domains in AIP1 and a conserved C2 domain of PKC. The amino acid residues in bold are Ca2+-binding sites. The K clusters in AIP1 are underlined and are mutated to A to generate KA1, KA2, and KA1/2 (mutations at both K clusters). (b) Mutations at the second K cluster significantly reduce ASK1 binding. FLAG-tagged AIP1-N, KA1, KA2, or KA1/2 ASK1-ΔN was cotransfected with ASK1 in ECs, and interaction of ASK1 with AIP1-N or mutants was examined by immunoprecipitation with anti-ASK1, followed by Western blot with anti-FLAG.