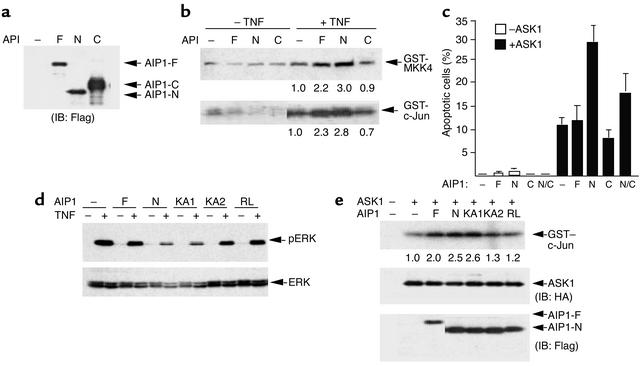
Figure 7.
AIP1 enhances TNF-α–induced ASK1 activity. (a and b) AIP1 enhances TNF-α–induced ASK1 and JNK activation. BAECs were transfected with vector control (–) or AIP1 constructs (AIP1-F, -N, or -C). Cell lysates were used to determine protein expression by Western blot with anti-FLAG (a) ASK1 and JNK activation were measured by an in vitro kinase assay (b). The relative ASK1 and JNK activities (setting TNF-α–treated vector control as 1.0) are indicated below each lane. (c) AIP1 enhances ASK1-induced EC apoptosis. BAECs were transfected with vector control (–) or AIP1 constructs (AIP1-F, AIP1-N, and AIP1-C) in the absence or presence of ASK1. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were stained with DAPI, and apoptotic cells with nucleus fragmentation were counted under a fluorescence microscope. The apoptotic rate is shown. Data presented are mean of three independent experiments. N/C, AIP1-N + AIP1-C. (d) AIP1 inhibits TNF-α–induced ERK activation. ECs were transfected with AIP1 constructs followed by TNF-α stimulation (10 ng/ml for 15 minutes). ERK activation was determined by Western blot with phospho-ERK antibody. Total ERK was determined by Western blot with anti-ERK. Similar results were obtained from two additional independent experiments. (e) ASK1 binding and the GAP activity of AIP1 are required for AIP1-enhanced ASK1 activation. AIP1 constructs were transfected into BAECs in the presence of HA-tagged ASK1. Protein expression was determined by Western blot with anti-HA (for ASK1) or anti-FLAG (for AIP1). ASK1-induced JNK activity was determined as described in b. Data shown are representative of three similar experiments.