Figure 2.
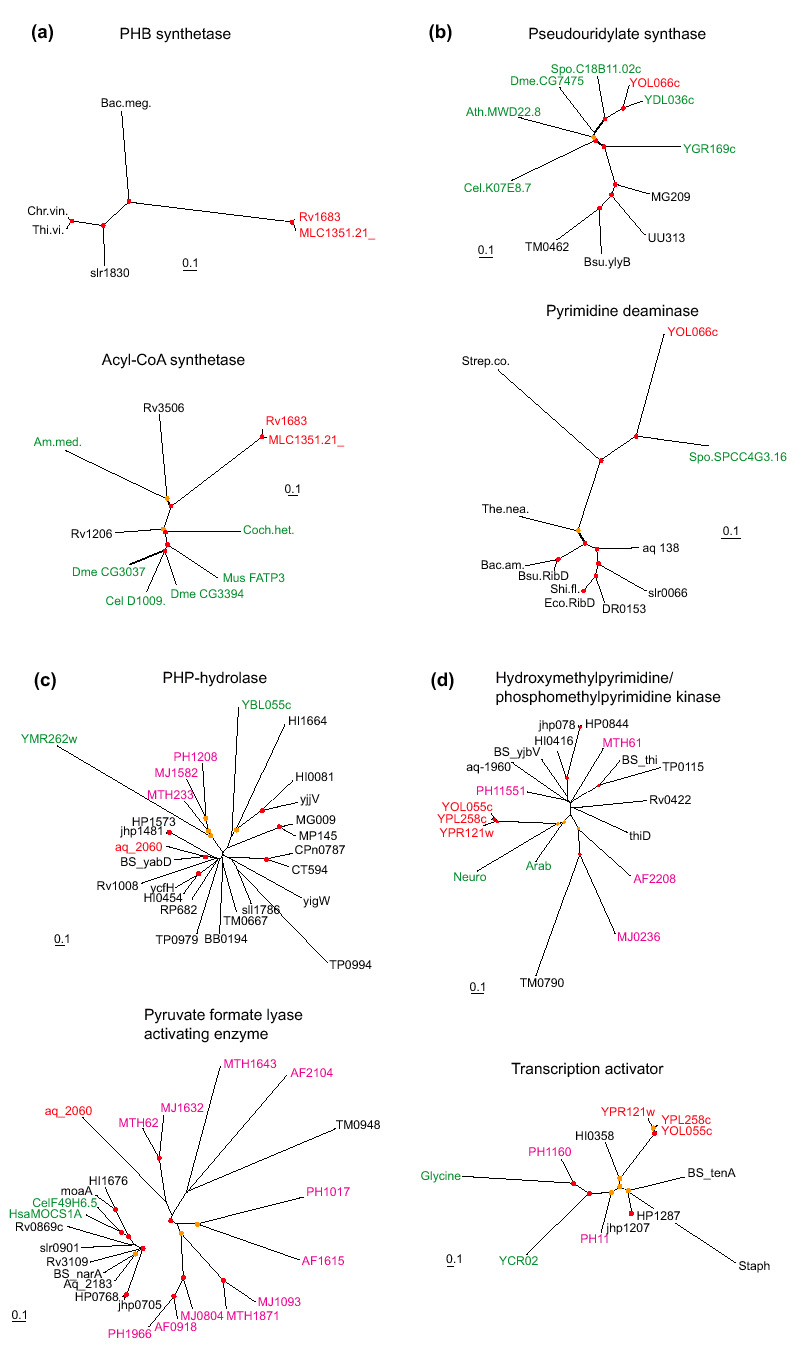
Examples of phylogenetic trees supporting the contribution of interkingdom horizontal gene transfer to the emergence of interkingdom domain fusions. The names of proteins from different primary kingdoms are color-coded: black, bacterial; pink, archaeal; green, eukaryotic; the domains involved in the apparent IKF are shown in red. Red circles show nodes with bootstrap support >70%, and yellow circles show nodes with 50-70% support. The bar unit corresponds to 0.1 substitutions per site (10 PAM). (a) IKF: Rv1683 (gi| 7476858) from M. tuberculosis. Fusion of a bacterial poly(3-hydroxy-butyrate) (PHB) synthase and eukaryotic very long chain acyl-CoA synthetase. Note the absence of eukaryotic homologs in the PHB synthase tree and of bacterial homologs other than the two from M. leprae in the acyl-CoA synthetase tree. (b) IKF: yeast YOL066c (gi|6324506). Fusion of a eukaryotic pesudouridylate synthetase with a bacterial pyrimidine deaminase. Note the absence of eukaryotic homologs, other than that from S. pombe, in the pyrimidine deaminase tree. (c) IKF: aq_2060 (gi|2984285) from Aquifex aeolicus. This protein is a fusion of a PHP superfamily hydrolase of apparent bacterial origin and a pyruvate formate-lyase activating enzyme of archaeal origin. (d) IKF: yeast YOL055c (gi|1419865), YPL258c (gi|2132251) and YPR121w (gi|2132289) from S. cerevisiae. Fusion of a eukaryotic phosphomethylpyrimidine kinase and a bacterial transcriptional activator. Species abbreviations: Bac.meg., Bacillus megaterium; Chr.vin., Chromatium vinosum; Thi.vi., Thiocystis violacea; Am.med., Amycolatopsis mediterranei; Coch.het., Cochliobolus heterostrophus; Dme, Drosophila melanogaster; Cel, Caenorhabditis elegans; Mus, Mus musculus; Spo, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Ath, Arabidopsis thaliana; Strep.co., Streptomyces coelicolor; The.nea., Thermotoga neapolitana; Bac. am, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; Shi.fl., Shigella flexneri; Hsa, Homo sapiens.
