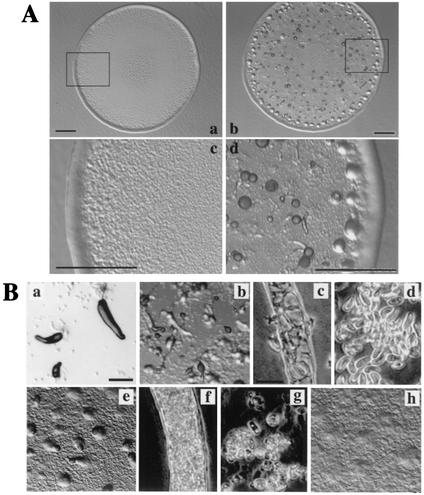
FIG. 3.
The development of mfeA-null cells cultivated in HL5 or on E. coli B/r. (A) Plaques formed from mfeA-null (a and c) and wild-type cells (b and d) on an E. coli lawn. Panels c and d give higher magnification of the images in the rectangles in panels a and b, respectively. Scale bars, 1 mm. All plaques formed from mfeA-null cells did not show any sign of multicellular development as seen in panels a and c. (B) Effects of culture conditions on development of the mutant cells on nonnutrient agar. The axenically grown mutant cells formed slugs (a) and fruiting bodies (b) with normal stalk cells (c) and spores (d). mfeA-null cells that had been cultivated on bacteria for 3 h often formed aberrant multicellular structures (e) that eventually developed into fruiting body-like structures with a stalk but filled with abnormal cells (f) and a globular mass atop the stalk, which consisted of a mixture of ellipsoidal cells or unhealthy amoebae (g). mfeA-null cells that had been cultivated for 24 h on bacterial lawn did not develop into multicellular structures on nonnutrient agar plates (h). Scale bars, 0.2 mm and 20 μm.