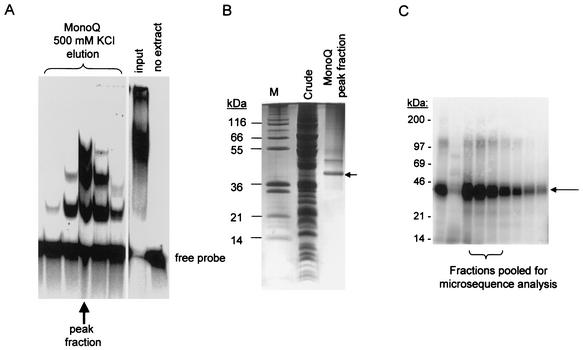
FIG. 1.
Isolation of LtRBP38 from mitochondrial extracts of L. tarentolae by using two different purification protocols. (A and B) Method 1 is a gel shift assay with a partially paired duplex RNA (substrate 3, panel C). Mitochondrial extracts were chromatographically enriched for RNA-binding activity by using Blue-Sepharose, heparin, and MonoQ columns. The final MonoQ column was developed with a 0 to 1 M KCl gradient. The collected fractions were used in the gel shift assay shown. (B) The 500 mM KCl peak fraction (indicated in panel A by an arrow) was analyzed on a SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the gel was stained with Coomassie blue. The fraction contained a major 38-kDa band (arrow) that was isolated and subjected to microsequencing. (C) Method 2 is a gel shift assay for RNA binding to single-stranded RNA using uniformly labeled T7-transcribed gRPS12-III gRNA as the probe. The mitochondrial extract was chromatographically enriched with Q-Sepharose, S-Sepharose, and MonoQ columns. The final MonoQ column was developed by using a gradient of 50 to 500 mM KCl, and the peak activity was subjected to UV cross-linking, RNase digestion, and SDS-gel electrophoresis. The major radioactively labeled cross-link migrated at 38 kDa as a single band (Fig. 1C). This band was eluted from the gel (pooled from lanes 3 to 5) and subjected to N-terminal sequencing. The sequence was identical to the predicted amino acid sequence of the protein isolated by method 1: 27 amino acids from the N terminus.