Abstract
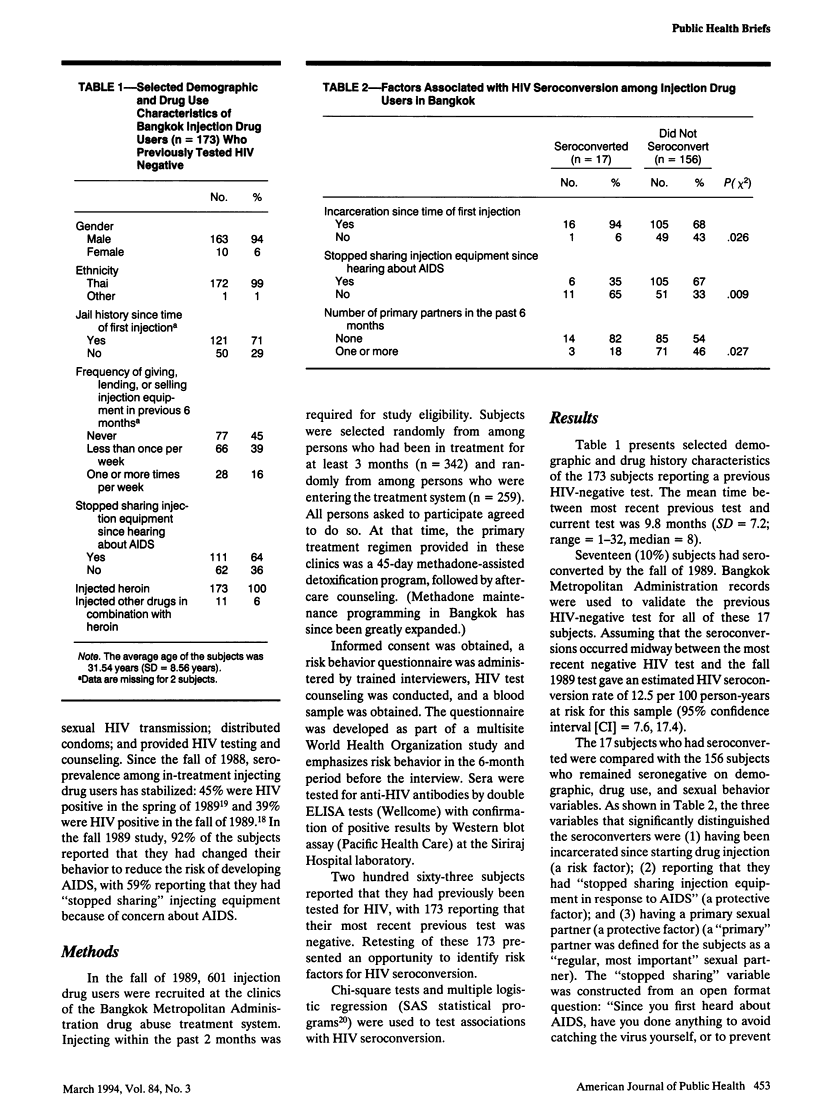
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) seroconversion was studied in a group of 173 injection drug users in Bangkok, Thailand, who had been previously tested for HIV and were interviewed and retested in the fall of 1989. Ten percent of the group had seroconverted. Two factors protected against HIV seroconversion: having stopped sharing injection equipment in response to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and having a regular sexual partner. The association between self-reported deliberate risk reduction and reduced HIV seroconversion among persons continuing to inject illicit drugs indicates that injection drug users can change their behavior in response to AIDS and will accurately report on the behavior change, and that the changes can protect against HIV infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. The New York Needle Trial: the politics of public health in the age of AIDS. Am J Public Health. 1991 Nov;81(11):1506–1517. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.11.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choopanya K., Vanichseni S., Des Jarlais D. C., Plangsringarm K., Sonchai W., Carballo M., Friedmann P., Friedman S. R. Risk factors and HIV seropositivity among injecting drug users in Bangkok. AIDS. 1991 Dec;5(12):1509–1513. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199112000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R., Choopanya K., Vanichseni S., Ward T. P. International epidemiology of HIV and AIDS among injecting drug users. AIDS. 1992 Oct;6(10):1053–1068. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199210000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R., Novick D. M., Sotheran J. L., Thomas P., Yancovitz S. R., Mildvan D., Weber J., Kreek M. J., Maslansky R. HIV-1 infection among intravenous drug users in Manhattan, New York City, from 1977 through 1987. JAMA. 1989 Feb 17;261(7):1008–1012. doi: 10.1001/jama.261.7.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs D., Unterweger B., Hausen A., Reibnegger G., Werner E. R., Hengster P., Hinterhuber H., Dierich M. P., Wachter H., Blattner W. A. Anti-HIV-1 antibodies, anti-HTLV-I antibodies and neopterin levels in parenteral drug addicts in the Austrian Tyrol. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(1):65–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käll K. I., Olin R. G. HIV status and changes in risk behaviour among intravenous drug users in Stockholm 1987-1988. AIDS. 1990 Feb;4(2):153–157. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199002000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lart R., Stimson G. V. National survey of syringe exchange schemes in England. Br J Addict. 1990 Nov;85(11):1433–1443. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1990.tb01626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loimer N., Presslich O., Hollerer E., Pakesch G., Pfersman V., Werner E. Monitoring HIV-1 infection prevalence among intravenous drug users in Vienna 1986-1990. AIDS Care. 1990;2(3):281–286. doi: 10.1080/09540129008257741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker J., Stoddard A. M., McCarthy E. The validity of self-reported HIV antibody test results. Am J Public Health. 1992 Apr;82(4):567–569. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.4.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. R., Skidmore C. A., Roberts J. J. HIV infection in intravenous drug users: a follow-up study indicating changes in risk-taking behaviour. Br J Addict. 1988 Apr;83(4):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1988.tb00484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum E. E., Hartel D., Selwyn P. A., Klein R. S., Davenny K., Rogers M., Feiner C., Friedland G. Risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus infection in intravenous drug users. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):874–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selik R. M., Castro K. G., Pappaioanou M. Racial/ethnic differences in the risk of AIDS in the United States. Am J Public Health. 1988 Dec;78(12):1539–1545. doi: 10.2105/ajph.78.12.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoek J. A., Coutinho R. A., van Haastrecht H. J., van Zadelhoff A. W., Goudsmit J. Prevalence and risk factors of HIV infections among drug users and drug-using prostitutes in Amsterdam. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):55–60. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


