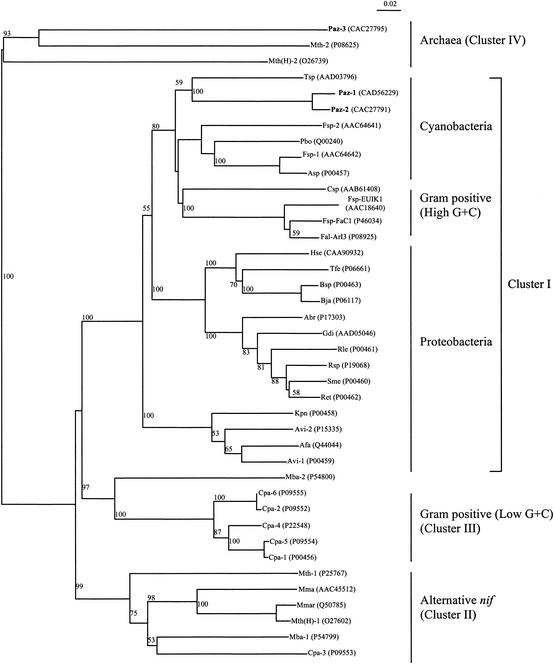
FIG. 3.
Tree showing phylogeny of NifH polypeptide sequences, constructed by the neighbor-joining method (27). Graphic representation of the tree was made using NJPlot software (23). The database accession numbers are indicated after the abbreviations. Cluster I to IV assignments are described elsewhere (5, 6). The data was analyzed with 100 bootstrap values. The values presented above the nodes are the bootstrap values generated. Bootstrap values below 50% are not shown. The scale bar represents 0.02 substitution per site. Abbreviations: Abr, Azospirillum brasilense; Afa, Alcaligenes faecalis; Asp, Nostoc sp. strain PCC7120; Avi, Azotobacter vinelandii; Bsp, Bradyrhizobium sp. strain ANU289; Bja, Bradyrhizobium japonicum; Cpa, Clostridium pasteurianum; Csp, Cyanothece sp. strain ATCC 51142; Fal-ArI3, Frankia alni strain ArI3; Fsp-EUIK1, Frankia sp. strain EUIK1; Fsp-FaC1, Frankia sp. strain FaC1; Fsp, Fischerella sp. strain UTEX1931; Gdi, Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus; Hse, Herbaspirillum seropedicae; Kpn, Klebsiella pneumoniae; Mba, Methanosarcina barkeri; Mma, Methanococcus maripaludis; Mth(H), Methanothermobacter thermoautotrophicus (ΔH); Mmar, Methanothermobacter marburgensis strain Marburg; Mth, Methanothermococcus thermolithotrophicus; Paz, Paenibacillus azotofixans; Pbo, Plectonema boryanum; Ret, Rhizobium etli; Rle, Rhizobium leguminosarum; Rsp, Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234; Sme, Sinorhizobium meliloti; Tfe, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans; Tsp, Trichodesmium sp. strain IMS101.