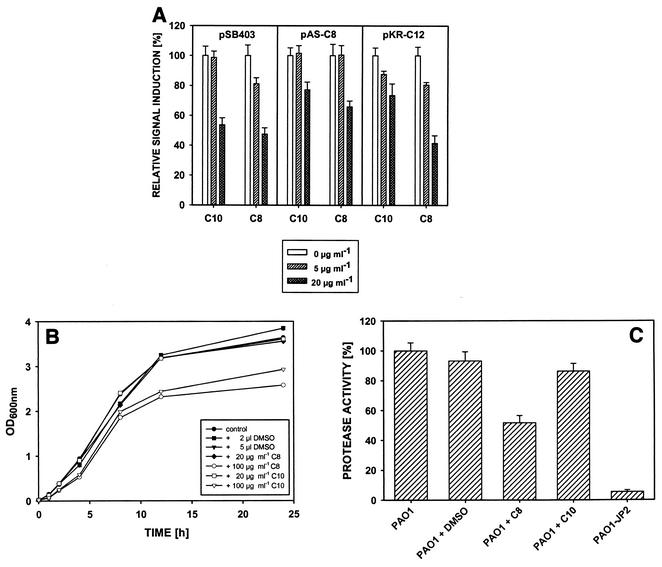
FIG. 3.
Interference of F. foliacea compounds 8 and 10 with AHL-dependent cell-cell communication. (A) Responses of different quorum-sensing reporter strains to the signal molecules and compounds 8 (C8) and 10 (C10). pKR-C12, P. putida harboring pKR-C12; pAS-C8, P. putida harboring pAS-C8; pSB403, E. coli harboring pSB403. The reporter strain signals (fluorescence and bioluminescence) in the absence of the compounds were defined as 100%. (B) Effects of compounds 8 and 10 on the growth of E. coli. The cultures were grown in the presence (20 or 100 μg/ml) or absence of compounds 8 and 10. Control cultures were supplemented with appropriate volumes of DMSO. OD600nm, optical density at 600 nm. (C) Effects of compounds 8 and 10 on expression of QS-regulated exoproteases of P. aeruginosa PAO1. Cultures of PAO1 were grown in the absence or presence of 20 μg of compound 8 or 10 per ml. P. aeruginosa lasI rhlI mutant PAO1-JP2, an AHL-deficient mutant, was used as a negative control. The protease activities of spent culture supernatants were determined with azocasein as the substrate. The data are means of three independent experiments. The proteolytic activity of PAO1 in the absence of the compounds was defined as 100%. The error bars indicate the standard errors of the means.