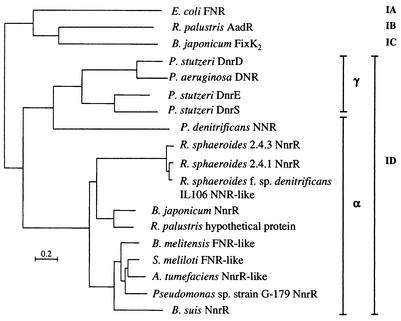
FIG. 5.
Phylogenetic tree of 15 FNR-like transcriptional activator proteins belonging to subgroup ID (14, 16, 39). For comparison, one representative reference protein of each subgroup IA, IB, and IC is included in the tree. Amino acid sequences were aligned with the program T-COFFEE (27; http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/TCoffee.html), and phylogenetic analyses were performed with the phylogeny inference package PHYLIP (13; http://bioweb.pasteur.fr/seqanal/phylogeny/phylip-uk.html). The scale bar represents a distance of 0.2 substitutions per position. Accession numbers of individual protein sequences are the following: E. coli FNR, AAC74416; R. palustris AAdR, Q01980; B. japonicum FixK2, CAA06287; P. stutzeri DnrD, CAC14591; P. aeruginosa DNR, BAA08744; P. stutzeri DnrE, CAB40906; P. stutzeri DnrS, CAB40908; P. denitrificans NNR, AAA69977; R. sphaeroides 2.4.3 NnrR, AAC44402; R. sphaeroides 2.4.1 NnrR, AAB69132; R. sphaeroides f. sp. denitrificans IL-106 NNR-like, AAD27624; B. japonicum NnrR, CAC38738; R. palustris NnrR-like, ZP_00008933; Brucella suis NnrR, AAN33482; Brucella melitensis FNR-like, NP_541964; Pseudomonas sp. strain G-179 NnrR, AAB96771; Sinorhizobium meliloti FNR-like, NP_435925; Agrobacterium tumefaciens NnrR-like, NP_534858.