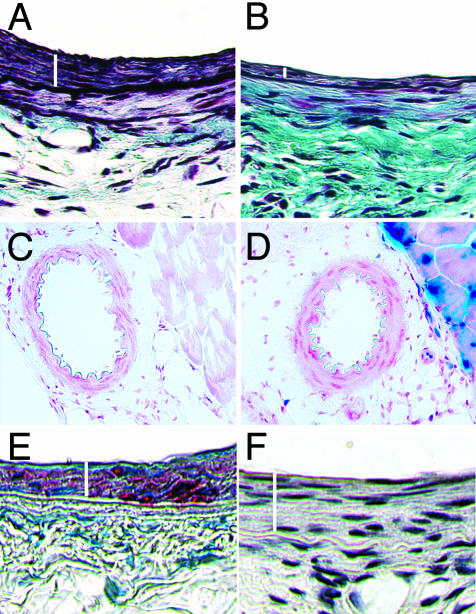
Figure 5.
Histological analysis of femoral arteries. Combined Mason’s trichrome elastin and hematoxylin-eosin staining of DOX− femoral artery (A) and DOX+ artery (B) 4 weeks after injury. White bars indicate the intimal area. The DOX+ artery shows substantially less intimal hyperplasia when compared to the DOX− artery. β-galactosidase staining of DOX− femoral artery (C) and DOX+ femoral artery (D) 2 days after induction with DOX. Neither DOX− nor DOX+ femoral artery show staining. Note the staining of skeletal muscle in the DOX+ artery. E: DOX− artery 4 weeks after injury showing actin staining in the intima and media (medial area underneath and adjacent to the intimal area shown by the white bar). F: DOX− artery 4 weeks after injury show absence to MOMA staining for macrophages. Original magnifications, ×400 (A, B).