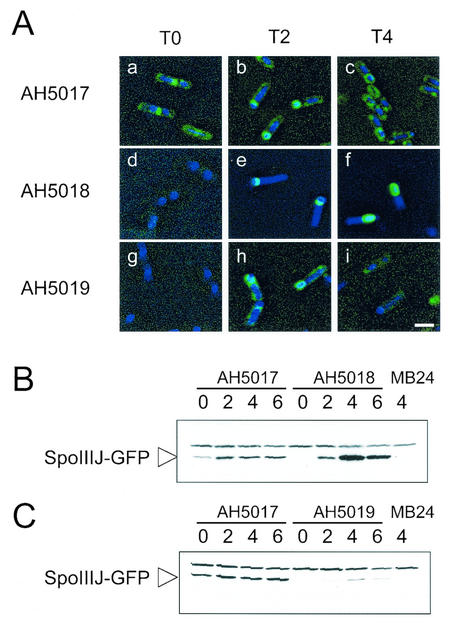
FIG. 6.
SpoIIIJ-GFP localization and accumulation. (A) Typical localization patterns of SpoIIIJ-GFP in the various strains at the indicated times. The strains were grown in DSM, and samples were taken throughout sporulation for observation by fluorescence microscopy with the DNA stain DAPI. Strains AH5017 (PspoIIIJ-spoIIIJ-gfp) (panels a to c), AH5018 (PspoIIQ-spoIIIJ-gfp) (panels d to f), and AH5019 (PspoIID-spoIIIJ-gfp) (panels g to i) were observed at the onset of sporulation (panels a, d, and g), at T2 (panels b, e, and h), and at T4 (panels c, f, and i). Bar, 2 mm. (B and C) Immunoblot analysis of SpoIIIJ-GFP accumulation in DSM in strains AH5017 (PspoIIIJ-spoIIIJ-gfp) and AH5018 (PspoIIQ-spoIIIJ-gfp) (B) and in strains AH5017 (PspoIIIJ-spoIIIJ-gfp) and AH5019 (PspoIID-spoIIIJ-gfp) (C). Results for strain AH5017 are repeated in panels B and C to allow direct comparison. Samples were collected at the end of the exponential phase of growth in DSM, which was defined as the onset of sporulation (lanes 0) and at 2, 4, and 6 h thereafter. Proteins (30 μg) were electrophoretically resolved on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, and GFP was detected with a polyclonal rabbit antibody (see Materials and Methods). The arrowhead indicates the position of the SpoIIIJ-GFP fusion protein. Another band with slower migration that is also found in MB24 represents a cross-reactive species. The last lane in panels B and C contains 30 μg of an extract prepared from a culture of the wild-type strain (MB24) at h 4 of sporulation in DSM.