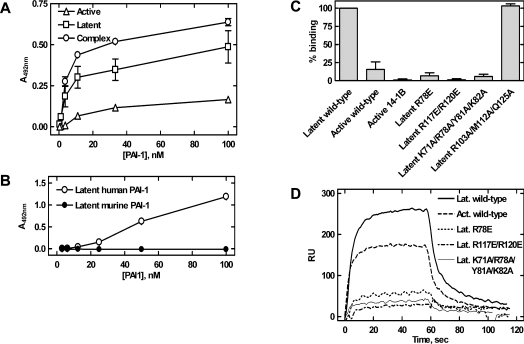
Figure 6. Localization of the paionin-1-binding site.
(A) Binding between recombinant PAI-1, active, latent or in complex with uPA (complex), and paionin-1 phage in ELISA format 2 (see the Experimental section). Latent PAI-1 was prepared by incubating active PAI-1 at 37 °C for 16 h and uPA–PAI-1 complex was prepared by incubating active PAI-1 with a 2-fold molar excess of uPA at room temperature for 30 min. Results are means±S.D., representative of two independent experiments with similar results, each performed in triplicate. (B) Binding between recombinant human or murine PAI-1 and paionin-1 phage in ELISA format 3 (see the Experimental section). Results are means±S.D., representative of two independent experiments with similar results, each performed in triplicate. (C) Biotin–paionin-1 peptide binding to recombinant PAI-1 variants in ELISA format 4 (see the Experimental section). PAI-114–1B (active 14-1B) is a stable active PAI-1 variant carrying four mutations [42], other PAI-1 variants are indicated by their mutations. Except for active PAI-1 (active wild-type) and PAI-114–1B (active 14-1B), the tested variants were in their latent conformation. Signals were normalized to those obtained with latent PAI-1. Results are means±S.D. for three independent experiments. (D) SPR sensorgrams for association and dissociation of PAI-1 variants to immobilized biotin–paionin-1 with a C-terminal GAKK extension. Except for active (Act.), the variants were in their latent (Lat.) conformation. Protein (700 nM) was applied at a flow rate of 5 μl/min and the sensorgrams were corrected by subtraction of the signals from a reference cell.