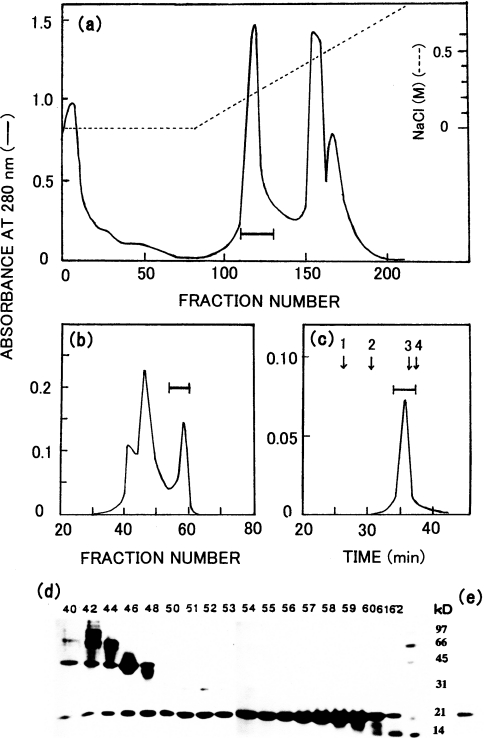
Figure 2. Isolation and purification of the 23 kDa protein (Copia proteinase) expressed in E. coli with pEC3.
(a) DEAE-cellulose chromatography. The solution of the solubilized inclusion body from E. coli with pEC3 was applied to a DEAE-cellulose column (2.8 cm diameter×32 cm long) at pH 7.9 and eluted with a linear gradient of 0–0.75 M NaCl in a total volume of 1 litre. The fraction size was 7.5 ml. (b) Sephacryl S-200 chromatography. The pooled fraction from the DEAE-cellulose chromatography was concentrated and applied to a Sephacryl S-200 column (3.1 cm diameter×145 cm long) at pH 7.9. The fraction size was 7.5 ml. (c) TSKgel G3000 SW chromatography. The pooled fraction from the Sephacryl S-200 column was submitted to the refolding procedure, and then applied to a TSKgel G3000 SW column at pH 5.5. Arrows indicate the elution positions of standard proteins: 1, BSA; 2, ovalbumin; 3, soybean trypsin inhibitor; 4, lysozyme. (d) SDS/PAGE of Sephacryl S-200 fractions. (e) SDS/PAGE of the pooled TSKgel G3000SW fraction. The same standard marker proteins were used in (d) and (e) as used in Figure 1. In each chromatographic run the fractions under the bar were pooled. The numbers above the gel in SDS/PAGE (d) indicate fraction numbers.