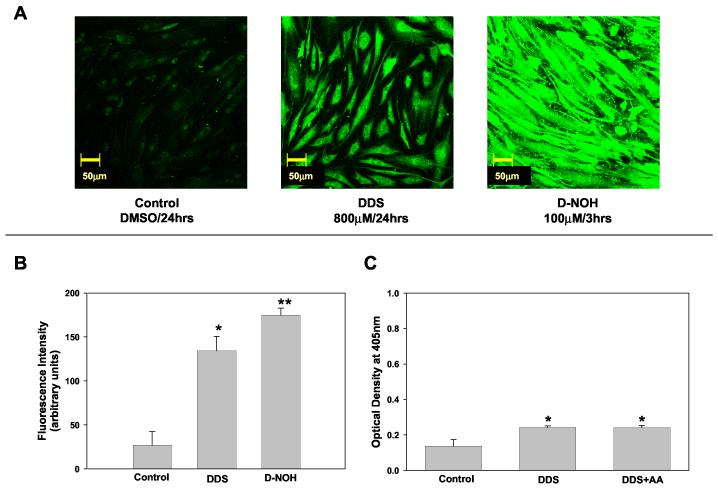
Figure 2.
Dapsone (DDS) - protein adducts formation in NHDF.
A) Detection of DDS protein adducts using confocal microscopy. NHDF cells (5x104cells/mL) were incubated with DDS (800 μM, 24 h) or D-NOH (100 μM, 3 h). Controls were exposed to the vehicle alone (dimethyl sulfoxide). At the end of the incubation cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde, permeabilized, immunostained, and imaged on a confocal microscope using 20X objective. B) Confocal Images were analyzed as detailed in the Materials and Methods and fluorescence intensity from a minimum of 3 view fields of 4 different slides (incubation) of each treatment (with 10 cells per field) were averaged and expressed as mean (+SD) fluorescence intensity (arbitrary units). Hence, each bar represents mean (SD) of the mean of 4 incubations with 30 measurements of fluorescence intensity for each incubation. Results were analyzed using ANOVA with Holm-Sidak method for multiple pairwise comparisons. *p< 0.05 compared to control, **p< 0.05 compared to control/DDS. C) Detection of DDS protein adducts formation using ELISA technique. NHDF cells were seeded at a density of 2x105cells/mL and incubated in the presence or absence of DDS 800 μM and/or Ascorbic Acid (AA) 2 mM. Data presented as optical density (OD) mean (+SD) of 4 separate incubations for each condition. Results were analyzed using ANOVA with Holm-Sidak method for multiple pairwise comparisons. *p<0.05 compared to control.