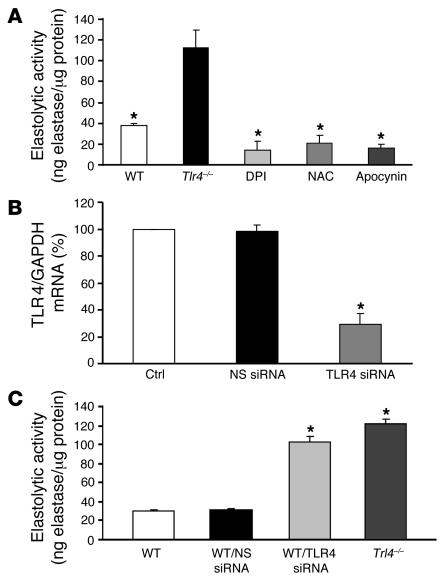
Figure 6. TLR4 deficiency leads to increased Nox-mediated elastolytic activity in MLECs.
(A) MLECs isolated from Tlr4–/– mice were treated with DPI (10 μM), NAC (100 μM), or apocynin (10 μM) for 24 hours, and elastolytic activity was assayed (n = 3). (B) TLR4 siRNA and nonspecific (NS) siRNA (80 nM) were transfected to WT MLECs, and TLR4 mRNA expression was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR (n = 3–5). Ctrl, untransfected control. (C) WT MLECs were transfected with nonspecific siRNA or TLR4 siRNA (80 nM), and elastolytic activity was assayed (n = 3). Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus Tlr4–/– (A), control and nonspecific siRNA (B), and WT and WT transfected with nonspecific siRNA (C).