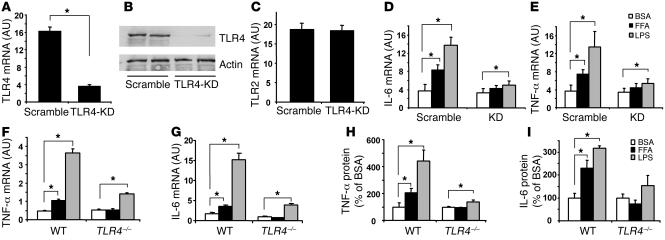
Figure 4. FFAs cause inflammatory response via TLR4 in adipocytes.
(A–C) Generation of an adipocyte model with specific TLR4 knockdown. 3T3-L1 preadipocytes were infected with retroviral short hairpin RNA interference (shRNAi) to knock down TLR4 (TLR4-KD), and cells were selected and then differentiated into adipocytes. TLR4 mRNA (A) and protein (B) and TLR2 mRNA (C) levels were evaluated by real-time RT-PCR and immunoblotting. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 6; *P < 0.05. (D and E) FFAs stimulate IL-6 and TNF-α mRNA expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via TLR4. TLR4-knockdown and scramble control adipocytes were treated with 400 μM FFA (palmitate and oleate mixture) or 100 ng/ml LPS for 12 hours. Real-time RT-PCR was conducted to measure the mRNA levels. n = 4; *P < 0.05. (F and G) FFAs stimulate TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA in WT but not in TLR4–/– adipocytes (n = 4; *P < 0.05). (H and I) FFAs stimulate TNF-α and IL-6 protein secretion in WT but not in TLR4–/– adipocytes (n = 4; *P < 0.05). Mouse adipocytes were isolated and precultured for 6 hours and then were treated with 400 μM FFA mixture for 16 hours. Real-time RT-PCR was used to measure mRNA levels. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.