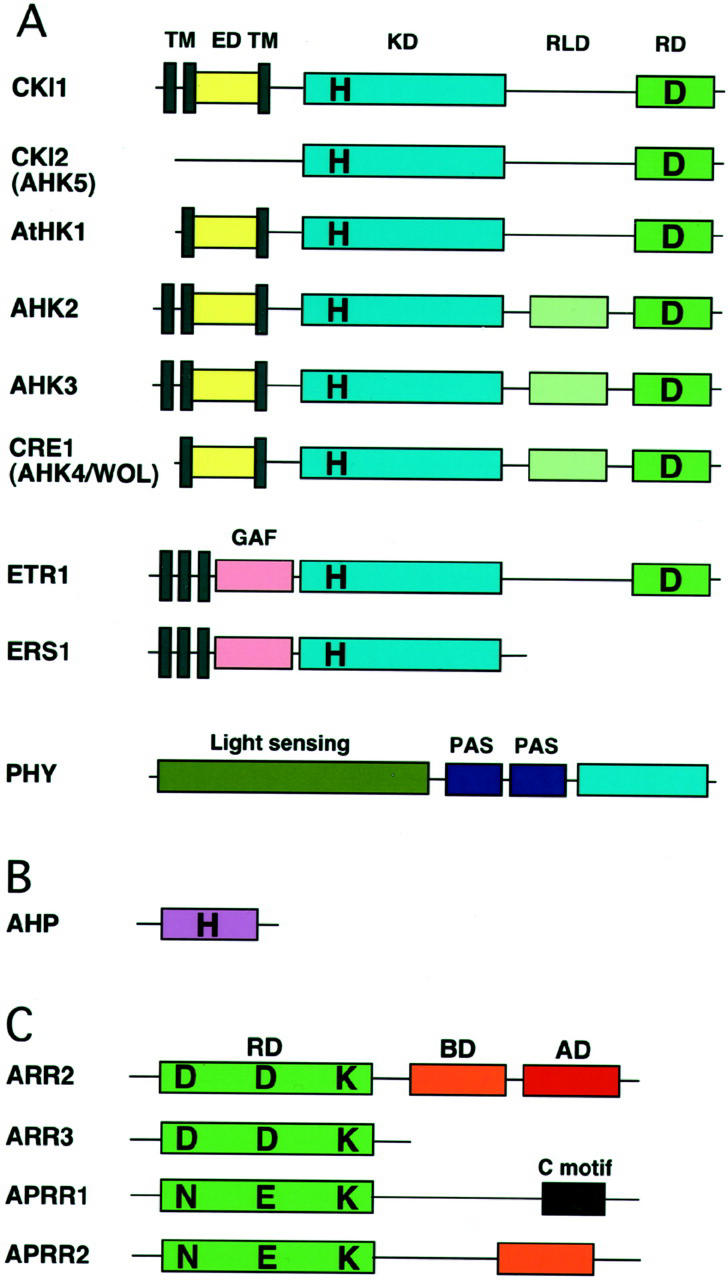
Figure 2.
Primary domain structure of representative two-component elements in Arabidopsis. A, CRE1/AHK4/WOL and CKI1 are similar in domain structure but quite diverged in amino acid sequence. ETR1 and ERS1 are representatives of the ethylene receptor family with/without a receiver domain. Phytochromes (PHY) are soluble proteins with similar overall structure and consisting of the light-sensing domain (the chromophore-binding domain), the PAS repeats, and a domain with His protein kinase homology. TM, Transmembrane domain; ED, extracellular putative input domain; KD, kinase domain; RD, receiver domain; RLD, receiver-like domain; H, His; D, Asp. B, His-containing phosphotransfer protein. C, Response regulators and response regulator-like proteins: ARR2, a B-type response regulator; ARR3, an A-type response regulator; and APRR1 and APRR2 (pseudo-type response regulators), response regulator-like proteins. ARR2 has a receiver domain followed by a DNA-binding domain (B motif) and a Pro-/Gln-rich transactivation domain, whereas ARR3 only carries a receiver domain. APRR1 and APRR2 have an atypical receiver domain similar to ARR2, but with N, E, and K motifs. In addition to a receiver-like domain, APRR1 and APRR2 have C and B motifs, respectively. Diagrams are not to scale. RD, Receiver domain; BD, DNA-binding B motif; AD, transactivation domain; D, Asp; N, Asn; E, Glu; K, Lys.