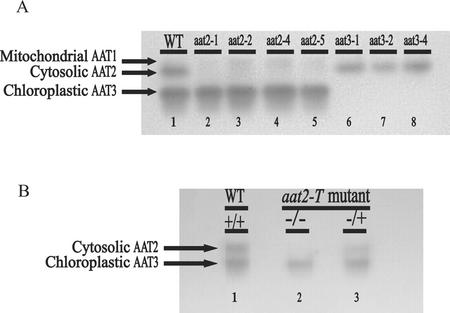
Figure 1.
AAT activity gel of wild-type and mutant plants. Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col; wild type) plant protein extracts run on native gels stained for AAT activity show two major and one minor AAT isoenzyme activity bands: mitochondrial AAT1, cytosolic AAT2, and chloroplastic AAT3. A, Lane 1 represents AAT activity in wild-type Arabidopsis, lanes 2 through 5 represent Arabidopsis mutants in cytosolic AAT2, and lanes 6 through 8 represent Arabidopsis mutants in chloroplastic AAT3. The additional new mutants, cytosolic aat2-5 and chloroplastic aat3-4, were isolated from individual pools of nitrosomethylurea (NMU)-mutagenized seed. B, AAT activity gel of an ASP2 T-DNA-inserted mutant (aat2-T) shows loss of cytosolic isoenzyme activity (lane 2) compared with wild type (lane 1). The mutant hemizygous for the ASP2 T-DNA insertion (lane 3) has one-half of the WT AAT2 activity and reflects the dose effect of having one wild-type ASP2 gene.