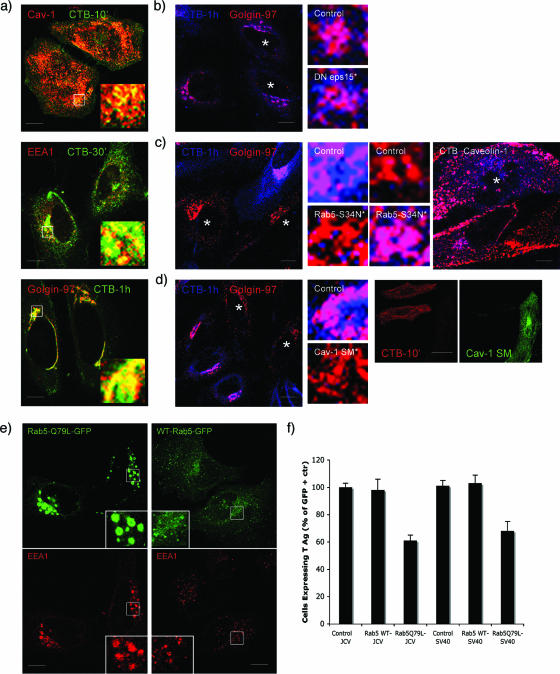
FIG. 2.
A pathway of intracellular trafficking from caveolae to early endosomes exists in SVG-A cells and is exploited by JCV. (a) Trafficking of CT-B through the cell. SVG-A cells on coverslips were allowed to internalize 200 pg of Alexa Fluor 647-labeled CT-B for the indicated times at 37°C. Cells were then fixed and stained with antibodies to caveolin-1 (caveolae), EEA1 (early endosomes), and Golgin-97 (Golgi), followed by Alexa Fluor 594-labeled secondary antibodies. The merged yellow signal indicated colocalization of CT-B with caveolin-1 at 10 min (top), with EEA1 at 30 min (middle), and with Golgin-97 at 60 min (bottom). (b) CT-B does not enter cells by clathrin-dependent endocytosis. SVG-A cells were transfected with an eps15 mutant that blocks clathrin assembly and then exposed to CT-B for 1 h. When clathrin endocytosis is blocked, CT-B can still efficiently be trafficked to the Golgi, as seen by the merged (magenta) signal. Stars indicate cells expressing dominant defective eps15. Enlarged images of a control cell and an eps15-expressing cell are shown. (c) Rab5 is required for proper CT-B trafficking. SVG-A cells were transfected with the Rab5-S34N mutant for 24 h. Cells were then exposed to CT-B for 1 h, fixed, and then stained for Golgin-97 or caveolin-1. In cells expressing the Rab5-S34N mutant, CT-B is retained in caveolae and fails to accumulate in the Golgi. Stars indicate cells expressing dominant defective Rab5S34N. Images at right show that expression of Rab5S34N prevents CT-B from trafficking from caveolae to early endosomes. (d) CT-B does not enter cells expressing a caveolin-1 scaffolding mutant (cav-1 SM). SVG-A cells were transfected with a caveolin-1 scaffolding mutant for 24 h. Cells were then exposed to CT-B for 1 h, fixed, and then stained for Golgin-97. In cells expressing the caveolin-1 scaffolding mutant, CT-B was unable to efficiently enter cells, and none is seen in the Golgi or even to enter the cell by 1 h. Stars indicate cells expressing a scaffolding mutant of caveolin-1. Panels at right indicate that CT-B fails to enter cells expressing the cav-1 scaffolding mutant. (e) Expression of the Rab5Q79L mutant causes endosomal fusion and the formation of enlarged endosomes. SVG-A cells on coverslips were transfected with the Rab-Q79L mutant for 24 h. Cells were then fixed and stained for the early endosomal antigen EEA1, followed by Alexa Fluor 594 secondary antibodies. (f) Expression of the Rab5-Q79L mutant inhibits JCV infection. SVG-A cells on coverslips were transfected with the Rab-Q79L mutant for 24 h and then infected with either JCV or SV40. Forty-eight hours postinfection, cells were fixed and stained for the early viral protein T antigen. The results are plotted as a percentage of nontransfected control cells from three independent experiments. Bars, 10 μm.