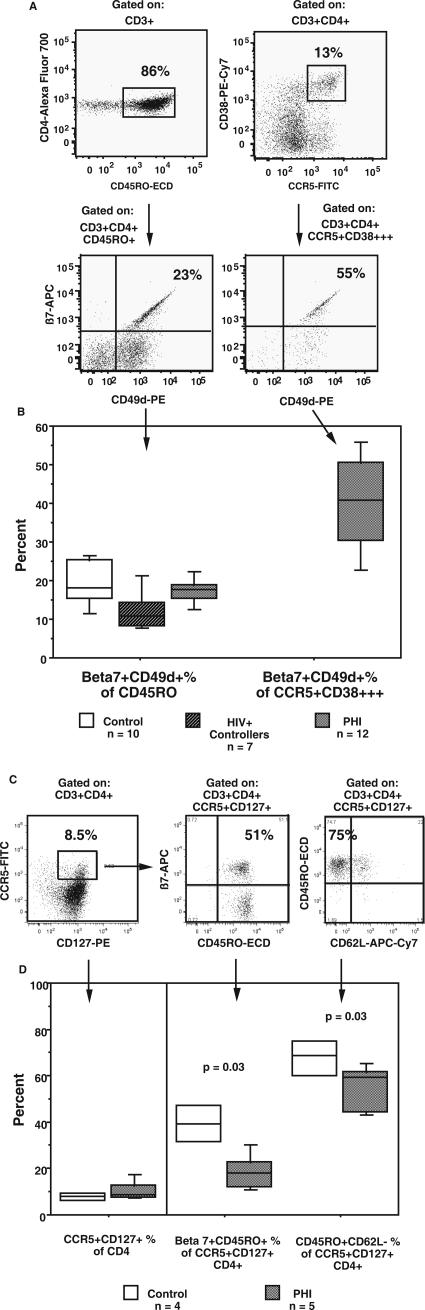
FIG. 3.
Gut-homing of CCR5+ CD4+ T cells during PHI. Fresh whole-blood samples were stained for CD3, CD4, CD45RO, CD62L, integrin β7, CD49d (integrin α4), CCR5, and CD38. Gut-homing CD4+ T cells were identified by coexpression of integrin β7 and CD49d. (A) The presence of integrin β7+CD49d+ cells within CD45RO+ and CCR5+CD38+++ CD4+ T-cell subsets is shown for 1 representative subject out of 12 subjects studied during PHI. The percentages of integrin β7+CD49d+ cells within their respective CD45RO+ and CCR5+CD38+++ CD4+ T-cell subsets are shown. (B) Box plots of integrin β7+CD49d+ cells as a percentage of CD45RO+CD4+ T cell for the three subject groups (left) and as a percentage of CCR5+CD38+++ CD4+ T cells for subjects with PHI only (right). Fresh whole-blood samples were also stained for CD3, CD4, CD45RO, CD62L, integrin β7, CCR5, and CD127. The CCR5+CD127+ subset present in a representative healthy adult control subject is shown in panel C, together with its expression of CD45RO, integrin β7, and CD62L. Box plots of CCR5+CD127+ cells as a percentage of CD4+ are shown at the left side of panel D, and β7+CD45RO+ and CD45RO+CD62L-negative cells as percentages of CCR5+CD127+ CD4+ T cells are also shown at the right side of the panel. Box plots depict the 90th, 75th, median, 25th, and 10th percentiles for each subject group, and the number of subjects in each group is shown. The P values shown are for subjects with PHI compared to those for healthy adult controls by a Mann-Whitney nonparametric test.