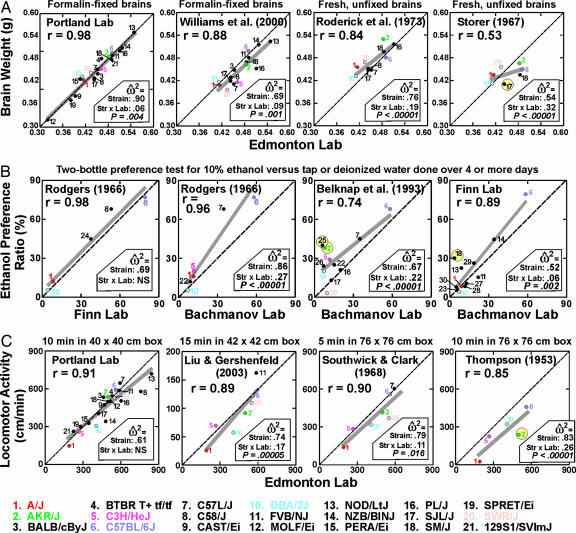
Fig. 1.
Correlations between means of inbred strains observed in different laboratories. The dashed line indicates identical results for two laboratories, and the gray line is the best fit of data from the y axis to data on the x axis, plotted for the actual range of data. When this line is above the dashed line, the means scores in laboratory Y were generally greater than for the corresponding strains tested in laboratory X. Numbers 1–21 correspond to strains shown at the bottom of the figure, with the most common strains shown as colored numerals. Effect sizes from the ANOVAs are shown for the strain main effect and strain-by-laboratory interaction. The significance (P) of the interaction effect is also indicated. NS denotes an interaction not significant at P = 0.05. (A) Brain weight measured in the Edmonton laboratory versus four other laboratories. Data for Edmonton and Portland were collected in 2002 and published in ref. 15. (B) Preference for 10% ethanol solution versus tap water. Nine additional strains not studied in the D.W. and J.C.C. laboratories were included in this set of comparisons (22, BALB/cJ; 23, BUB/BnJ; 24, C57BLKS/J; 25, CBA/J; 26, CE/J; 27, I/LnJ; 28, LP/J; 29, RIIIS/J; 30, SEA/GnJ). (C) Locomotor activity in Edmonton versus four other laboratories, scaled to centimeters per minute.