Figure 3.
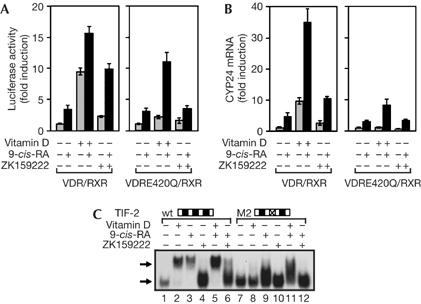
9-cis-retinoic acid restores the transcriptional activity of mutant vitamin D receptor/retinoid X receptor heterodimers and confers agonistic activity to ZK159222. (A) Reporter activity in 293-T cells expressing wild-type VDR/RXR or a heterodimer of RXR with the E420Q VDR mutant. (B) cyp24 messenger RNA levels measured in the same groups after 4 h incubation with vitamin D, ZK159222 and/or 9-cis-RA, as indicated. (C) Electrophoretic mobility-shift assays with the native VDR/RXR heterodimer and either wild-type (wt) TIF-2 or the mutant in the second LXXLL motif (M2). 9-cis-RA, 9-cis-retinoic acid; RXR, retinoid X receptor; VDR, vitamin D receptor.
