Figure 3.
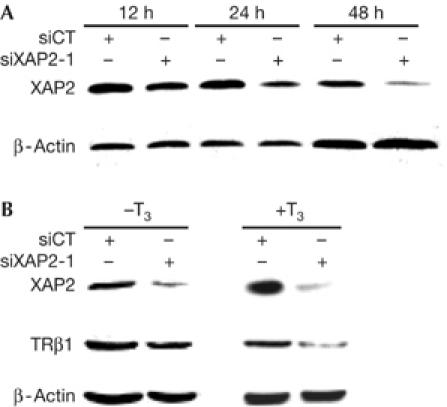
In vitro hepatitis virus B X-associated protein 2 small inhibitory RNA experiments. (A) Inhibition of XAP2 by siRNA: HC11 cells were transiently transfected with siRNA against mouse XAP2 (siXAP2-1). The cells were then collected after 12, 24 or 48 h and whole-cell extracts were prepared and fractionated on a 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel. Levels of protein expression were examined by western blot analysis using XAP2 or β-actin antibodies. (B) The stability of TRβ1 is affected by the absence of XAP2: P19 cells were transiently transfected with scrambled siRNA (siCT) or siRNA against mouse XAP2 (siXAP2-1) and grown for 48 h. The cells were then incubated (+T3) or not (−T3) with 1 μM of T3 for 2 h. WCEs were prepared and fractionated on a 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel. The stability of TRβ1 was detected by western blot analysis using TRβ1 antibody. XAP2 and β-actin antibodies were used as controls. siRNA, small inhibitory RNA; T3, triiodothyronine; TRβ1, thyroid hormone receptor subtype; XAP2, hepatitis virus B X-associated protein 2.
