Figure 1.
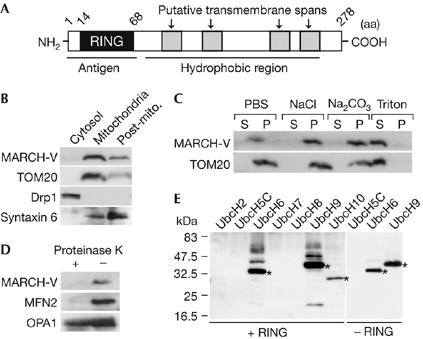
Characterization of MARCH-V. (A) Schematic drawing of the potential structure of MARCH-V. (B) The cytosol, mitochondria and post-mitochondria (Post-mito.) fractions (15 μg of protein) of COS7 cells were analysed by western blotting with antibodies to MARCH-V, TOM20, Drp1 and syntaxin 6 (a Golgi/endosomal protein). (C) The total membrane fractions of COS7 cells were incubated with PBS, 1 M NaCl, 0.1 M Na2CO3 (pH 11) or 1% Triton X-100 for 1 h on ice. After ultracentrifugation, the supernatant (S) and pellets (P; 20 μg of protein each) were analysed by western blotting. (D) The mitochondrial fractions were incubated with (+) or without (−) 100 μg/ml proteinase K for 1 h on ice. After quenching proteolysis by addition of phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride (1 mM final), the mitochondria were pelleted, dissolved in SDS sample buffer and analysed by western blotting. (E) Reaction mixtures containing E1, E2 indicated above the lanes and ubiquitin (Ub) were incubated in the presence (+RING) or absence (−RING) of glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins of the MARCH-V RING finger for 2 h at 30°C. Ubiquitinated materials were detected by western blotting with anti-Ub antibody. Asterisks indicate Ub-charged E2s.
