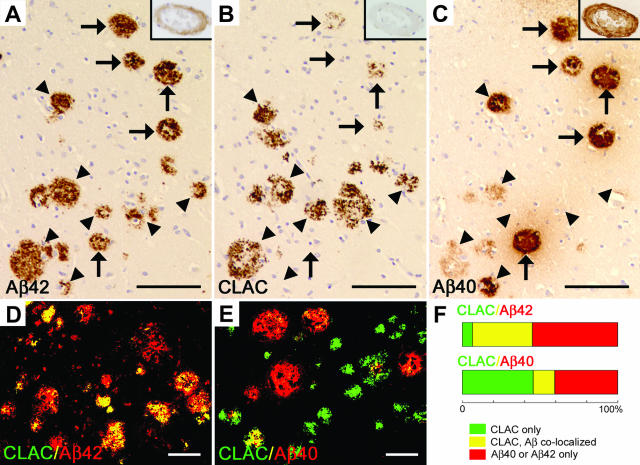
Figure 1.
Immunohistochemistry of Aβ42, CLAC and Aβ40 in the frontal neocortex of AD brain. A-C: Six-μm thick serial sections were immunostained with mAbs BC05 (Aβ42, A), 9D2 (CLAC, B), or BA27 (Aβ40, C). Arrowheads show Aβ42/CLAC-positive SP that are negative or only weakly positive for Aβ40, and arrows indicate Aβ40-positive SP that are negative or only weakly positive for CLAC. Insets show immunostaining of CAA in the subarchnoid space. Bar, 100 μm. D–E: Double immunofluorescence labeling of 50-μm thick floating sections for CLAC (anti-pyroGlu113, green) and Aβ42 (BC05, red) (D) or Aβ40 (BA27, red) (E), viewed by confocal microscopy. Bar, 50 μm (F). Relative ratios of percentage areas of SP that are CLAC-positive, Aβ42 or 40-negative (green), CLAC- and Aβ42 or 40-positive (yellow) or CLAC-negative, Aβ42 or 40-positive (red), in sections stained as in D (for Aβ42) or E (for Aβ40). Average levels in eight AD cases fixed in 10% formalin for 24 hours are shown. Note that the total SP areas (100%) correspond to those positive for CLAC plus Aβ42 in the upper bar, and CLAC plus Aβ40 in the lower bar, respectively.