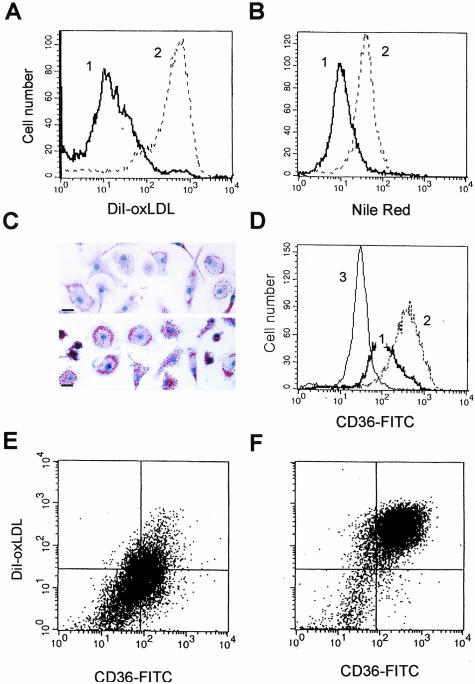
Figure 4.
Ligation of αVβ3 integrin on differentiated MDMs decreases DiI-oxLDL uptake and prevents oxLDL-induced foam cell formation via a mechanism requiring down-regulation of CD36 expression. MDMs (5 to 9 days of culture in vitro) were harvested and reseeded on immobilized antibodies to αVβ3 integrin (thick line) or control isotype-matched IgG1 (dotted line), and analyzed by flow cytometry 24 hours after reseeding. A: DiI-oxLDL uptake by MDMs after 3 hours of incubation with 5 μg/ml of labeled oxLDL. B: Lipid accumulation in cholesterol storage vacuoles induced by incubation with 50 μg/ml of oxLDL for 48 hours revealed by Nile Red staining. C: Reduction of foam cell formation in vitro induced by incubation with oxLDL (50 μg/ml) for 48 hours of MDMs reseeded on immobilized anti-αVβ3 mAb. Top: MDMs reseeded on immobilized anti-αVβ3 mAb. Bottom: MDM reseeded on immobilized control IgG1. Oil Red O lipid staining (red), hematoxylin nuclear counterstain (blue). D: Down-regulation of CD36 surface expression on MDMs induced by αVβ3 ligation revealed by staining with FITC-labeled mAb to CD36 and after analysis by flow cytometry (thin line shows isotype-matched control). E and F: CD36 surface expression (x axis) and DiI-oxLDL uptake (y axis) by MDMs reseeded on αVβ3 integrin antibodies (E) or control IgG1 (F). Scale bars, 20 μm.