Figure 2.
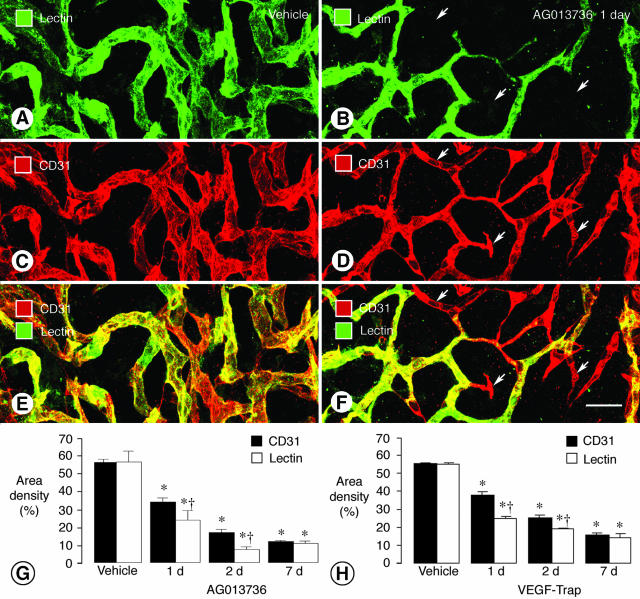
Reduction in tumor vessel patency and blood flow after inhibition of VEGF signaling. Confocal microscopic images of tumor vessels in RIP-Tag2 mice treated with vehicle (A, C, E) or AG013736 (B, D, F) for 1 day and injected with lectin before fixation by vascular perfusion. Lectin staining (A, green) of blood vessels in vehicle-treated tumor closely matches CD31 immunoreactivity (C, red). However, after treatment with AG013736, multiple vessels (arrows) lack lectin staining (B, green) but have CD31 immunoreactivity (D, red), indicating loss of vessel patency. Vessels without flow appear red in merged images (E, F). Bar graphs show area density (%) of lectin staining and CD31 immunoreactivity in vessels of RIP-Tag2 tumors after treatment for 1, 2, or 7 days with AG013736 (G) or VEGF-Trap (H) or their respective vehicle. After 1 or 2 days of treatment by either agent, the area density of lectin staining is significantly less than the amount of CD31 immunoreactivity. By 7 days, this discrepancy no longer exists, suggesting that the surviving vessels have blood flow. *, Different from vehicle (P < 0.05). †, Different from CD31 (P < 0.05). Scale bar, 25 μm.